Page 111 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 111
Salivary Glands 101
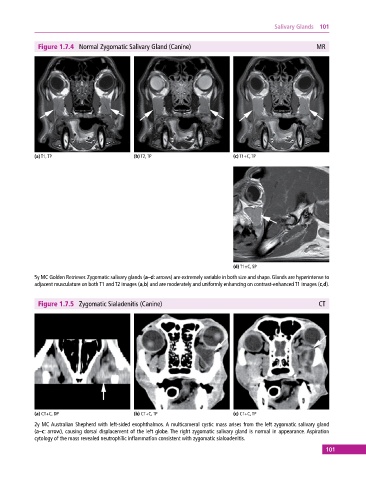
Figure 1.7.4 Normal Zygomatic Salivary Gland (Canine) MR
(a) T1, TP (b) T2, TP (c) T1+C, TP
(d) T1+C, SP
5y MC Golden Retriever. Zygomatic salivary glands (a–d: arrows) are extremely variable in both size and shape. Glands are hyperintense to
adjacent musculature on both T1 and T2 images (a,b) and are moderately and uniformly enhancing on contrast‐enhanced T1 images (c,d).
Figure 1.7.5 Zygomatic Sialadenitis (Canine) CT
(a) CT+C, DP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
2y MC Australian Shepherd with left‐sided exophthalmos. A multicameral cystic mass arises from the left zygomatic salivary gland
(a–c: arrow), causing dorsal displacement of the left globe. The right zygomatic salivary gland is normal in appearance. Aspiration
cytology of the mass revealed neutrophilic inflammation consistent with zygomatic sialoadenitis.
101