Page 166 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 166
156 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
originating in or caudal to the fourth ventricle will tend Postulated causes include intraventricular hemorrhage
to produce uniform ventricular distension, whereas and ventriculitis with cells or debris causing obstruction
obstruction in the third or lateral ventricles or in the of the valvular flow mechanism of individual villi.
interventricular foramina may produce asymmetrical, Chronic hydrocephalus also appears to diminish resorp-
regional, or focal ventricular distension (Figures 2.1.6, tive function of the villi. 11
2.1.7). 2,6–10
Communicating (nonobstructive) Hydrocephalus from CSF overproduction
hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus from overproduction of CSF is thought
to occasionally occur in some patients with functional
Impaired CSF resorption choroid plexus tumors in which the abnormally high
Impaired CSF resorption is thought to occur with rate of CSF production exceeds the rate of resorption
diminished resorptive capacity of the arachnoid villi. (Figure 2.1.8). 12
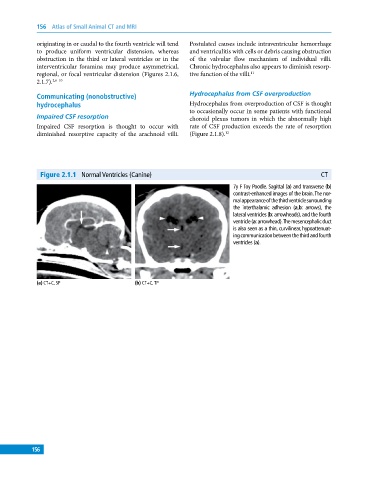
Figure 2.1.1 Normal Ventricles (Canine) CT
7y F Toy Poodle. Sagittal (a) and transverse (b)
contrast‐enhanced images of the brain. The nor-
mal appearance of the third ventricle surrounding
the interthalamic adhesion (a,b: arrows), the
lateral ventricles (b: arrowheads), and the fourth
ventricle (a: arrowhead). The mesencephalic duct
is also seen as a thin, curvilinear, hypoattenuat-
ing communication between the third and fourth
ventricles (a).
(a) CT+C, SP (b) CT+C, TP
156