Page 161 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 161
Thyroid and Parathyroid 151
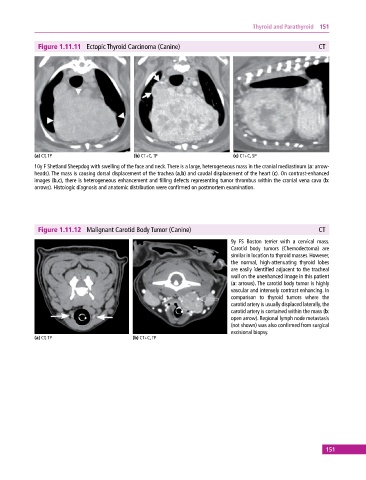
Figure 1.11.11 Ectopic Thyroid Carcinoma (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, SP
10y F Shetland Sheepdog with swelling of the face and neck. There is a large, heterogeneous mass in the cranial mediastinum (a: arrow-
heads). The mass is causing dorsal displacement of the trachea (a,b) and caudal displacement of the heart (c). On contrast‐enhanced
images (b,c), there is heterogeneous enhancement and filling defects representing tumor thrombus within the cranial vena cava (b:
arrows). Histologic diagnosis and anatomic distribution were confirmed on postmortem examination.
Figure 1.11.12 Malignant Carotid Body Tumor (Canine) CT
9y FS Boston terrier with a cervical mass.
Carotid body tumors (Chemodectoma) are
similar in location to thyroid masses. However,
the normal, high‐attenuating thyroid lobes
are easily identified adjacent to the tracheal
wall on the unenhanced image in this patient
(a: arrows). The carotid body tumor is highly
vascular and intensely contrast enhancing. In
comparison to thyroid tumors where the
carotid artery is usually displaced laterally, the
carotid artery is contained within the mass (b:
open arrow). Regional lymph node metastasis
(not shown) was also confirmed from surgical
excisional biopsy.
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP
151