Page 19 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 19
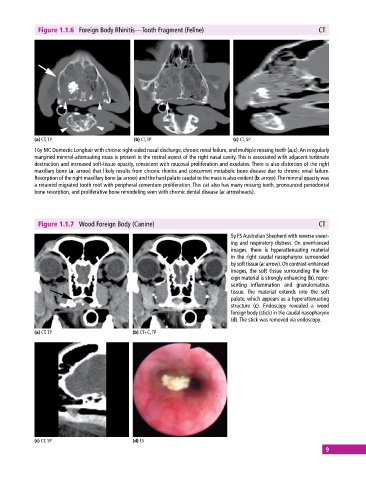
Figure 1.1.6 Foreign Body Rhinitis—Tooth Fragment (Feline) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP (c) CT, SP
16y MC Domestic Longhair with chronic right‐sided nasal discharge, chronic renal failure, and multiple missing teeth (a,c). An irregularly
margined mineral‐attenuating mass is present in the rostral aspect of the right nasal cavity. This is associated with adjacent turbinate
destruction and increased soft‐tissue opacity, consistent with mucosal proliferation and exudates. There is also distortion of the right
maxillary bone (a: arrow) that likely results from chronic rhinitis and concurrent metabolic bone disease due to chronic renal failure.
Resorption of the right maxillary bone (a: arrow) and the hard palate caudal to the mass is also evident (b: arrow). The mineral opacity was
a retained migrated tooth root with peripheral cementum proliferation. This cat also has many missing teeth, pronounced periodontal
bone resorption, and proliferative bone remodeling seen with chronic dental disease (a: arrowheads).
Figure 1.1.7 Wood Foreign Body (Canine) CT
5y FS Australian Shepherd with reverse sneez-
ing and respiratory distress. On unenhanced
images, there is hyperattenuating material
in the right caudal nasopharynx surrounded
by soft tissue (a: arrow). On contrast‐enhanced
images, the soft tissue surrounding the for-
eign material is strongly enhancing (b), repre-
senting inflammation and granulomatous
tissue. The material extends into the soft
palate, which appears as a hyperattenuating
structure (c). Endoscopy revealed a wood
foreign body (stick) in the caudal nasopharynx
(d). The stick was removed via endoscopy.
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP
(c) CT, SP (d) ES
9