Page 41 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 41
Ear 31
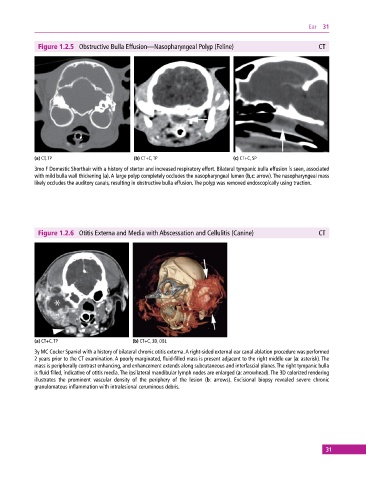
Figure 1.2.5 Obstructive Bulla Effusion—Nasopharyngeal Polyp (Feline) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, SP
3mo F Domestic Shorthair with a history of stertor and increased respiratory effort. Bilateral tympanic bulla effusion is seen, associated
with mild bulla wall thickening (a). A large polyp completely occludes the nasopharyngeal lumen (b,c: arrow). The nasopharyngeal mass
likely occludes the auditory canals, resulting in obstructive bulla effusion. The polyp was removed endoscopically using traction.
Figure 1.2.6 Otitis Externa and Media with Abscessation and Cellulitis (Canine) CT
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, 3D, OBL
3y MC Cocker Spaniel with a history of bilateral chronic otitis externa. A right‐sided external ear canal ablation procedure was performed
2 years prior to the CT examination. A poorly marginated, fluid‐filled mass is present adjacent to the right middle ear (a: asterisk). The
mass is peripherally contrast enhancing, and enhancement extends along subcutaneous and interfascial planes. The right tympanic bulla
is fluid filled, indicative of otitis media. The ipsilateral mandibular lymph nodes are enlarged (a: arrowhead). The 3D colorized rendering
illustrates the prominent vascular density of the periphery of the lesion (b: arrows). Excisional biopsy revealed severe chronic
granulomatous inflammation with intralesional ceruminous debris.
31