Page 91 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 91
Orbit 81
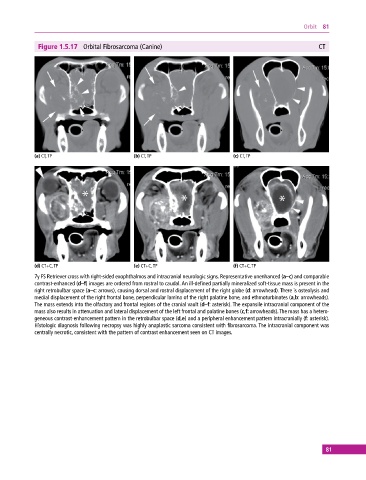
Figure 1.5.17 Orbital Fibrosarcoma (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT, TP (c) CT, TP
(d) CT+C, TP (e) CT+C, TP (f) CT+C, TP
7y FS Retriever cross with right‐sided exophthalmos and intracranial neurologic signs. Representative unenhanced (a–c) and comparable
contrast‐enhanced (d–f) images are ordered from rostral to caudal. An ill‐defined partially mineralized soft‐tissue mass is present in the
right retrobulbar space (a–c: arrows), causing dorsal and rostral displacement of the right globe (d: arrowhead). There is osteolysis and
medial displacement of the right frontal bone, perpendicular lamina of the right palatine bone, and ethmoturbinates (a,b: arrowheads).
The mass extends into the olfactory and frontal regions of the cranial vault (d–f: asterisk). The expansile intracranial component of the
mass also results in attenuation and lateral displacement of the left frontal and palatine bones (c,f: arrowheads). The mass has a hetero-
geneous contrast‐enhancement pattern in the retrobulbar space (d,e) and a peripheral enhancement pattern intracranially (f: asterisk).
Histologic diagnosis following necropsy was highly anaplastic sarcoma consistent with fibrosarcoma. The intracranial component was
centrally necrotic, consistent with the pattern of contrast enhancement seen on CT images.
81