Page 97 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 97
Globe 87
to the vitreous (Figure 1.6.7). Round cell neoplasia Cataracts/lens luxation
such as lymphoma can also primarily involve the eye Cataracts are a degenerative disease of the lens that
(Figure 1.6.8). Metastatic disease due to other neoplasms results in increased density and opacification. On CT
can also occur. Neoplasia should be considered in images, cataracts appear as hyperattenuating strands
patients with ocular hemorrhage where there is a clear within the lens, which can progress to involve the entire
fluid–fluid interface on MR images (Figure 1.6.9). lens (Figure 1.6.12). On MR images, the lens becomes
decreased in signal intensity (Figure 1.6.13). The lens is
Degenerative disorders normally hyperattenuating to the vitreous on CT images
and hypointense on MR images. Deformation of the
Retinal detachment shape of the lens can also occur with cataract formation.
Retinal detachment is uncommon in cats but may be Glaucoma can result in luxation of the lens into the
caused by bullous or effusive mechanisms, a tear with vitreous chamber (Figure 1.6.13).
vitreous filling the space between the retinal and choroid,
or contraction of postinflammatory fibrous strands in Prostheses
the vitreous pulling the retina anteriorly. The CT Some patients are fitted with ocular prostheses following
9
appearance of retinal detachment is a V‐shaped linear enucleation. If CT or MR imaging is performed, charac
structure (shaped like seagull wings) with the apex cen teristic artifacts may occur. Silicone‐based prostheses
tered at the optic disc (Figure 1.6.10). Hyperattenuating may contain pigments to mimic brown or black eye color.
material between the retina and the choroid may indicate In one study, the brown‐pigmented prosthesis contained
proteinaceous fluid or hemorrhage. Bullous retinal iron oxide or titanium dioxide, producing susceptibility
10
detachment due to fluid accumulation has been reported artifact. A black prosthesis was pigmented with carbon
in cats with hypertension. On MR images, the fluid black and did not produce ferromagnetic artifact, with no
9
external to the retina is hyperintense on T1 and T2 signal on any sequence (Figure 1.6.14). On CT images,
11
images (Figure 1.6.11). the prostheses tend to be hyperattenuating (Figure 1.6.15).
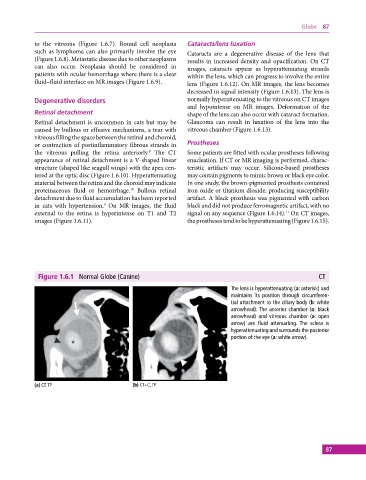
Figure 1.6.1 Normal Globe (Canine) CT
The lens is hyperattenuating (a: asterisk) and
maintains its position through circumferen-
tial attachment to the ciliary body (b: white
arrowhead). The anterior chamber (a: black
arrowhead) and vitreous chamber (a: open
arrow) are fluid attenuating. The sclera is
hyperattenuating and surrounds the posterior
portion of the eye (a: white arrow).
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP
87