Page 108 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 108
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
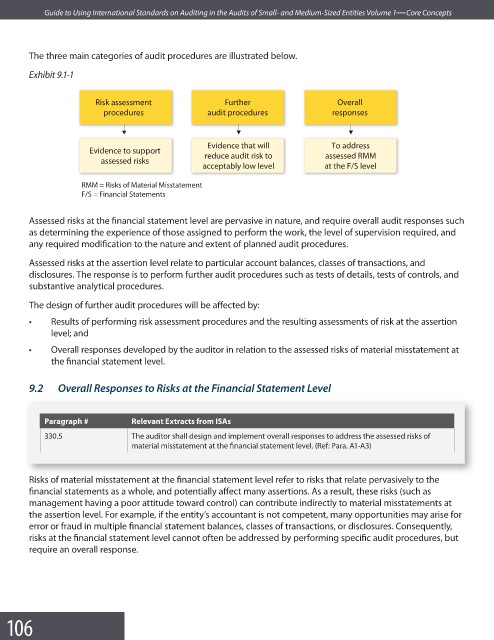
The three main categories of audit procedures are illustrated below.
Exhibit 9.1-1
Risk assessment Further Overall
procedures audit procedures responses
Evidence that will To address
Evidence to support
reduce audit risk to assessed RMM
assessed risks
acceptably low level at the F/S level
RMM = Risks of Material Misstatement
F/S = Financial Statements
Assessed risks at the financial statement level are pervasive in nature, and require overall audit responses such
as determining the experience of those assigned to perform the work, the level of supervision required, and
any required modification to the nature and extent of planned audit procedures.
Assessed risks at the assertion level relate to particular account balances, classes of transactions, and
disclosures. The response is to perform further audit procedures such as tests of details, tests of controls, and
substantive analytical procedures.
The design of further audit procedures will be aff ected by:
• Results of performing risk assessment procedures and the resulting assessments of risk at the assertion
level; and
• Overall responses developed by the auditor in relation to the assessed risks of material misstatement at
the financial statement level.
9.2 Overall Responses to Risks at the Financial Statement Level
Paragraph # Relevant Extracts from ISAs
330.5 The auditor shall design and implement overall responses to address the assessed risks of
material misstatement at the financial statement level. (Ref: Para. A1-A3)
Risks of material misstatement at the financial statement level refer to risks that relate pervasively to the
financial statements as a whole, and potentially affect many assertions. As a result, these risks (such as
management having a poor attitude toward control) can contribute indirectly to material misstatements at
the assertion level. For example, if the entity’s accountant is not competent, many opportunities may arise for
error or fraud in multiple financial statement balances, classes of transactions, or disclosures. Consequently,
risks at the financial statement level cannot often be addressed by performing specific audit procedures, but
require an overall response.
106