Page 112 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 112
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
Management override and fraudulent revenue recognition are presumed to be significant risks (see Volume 2,
Chapter 10 of this Guide) and addressed as such. As a result, there are certain audit procedures that would be
performed in every audit. These are outlined in the ISA extracts quoted above. Some additional comments
are included in the following exhibit.
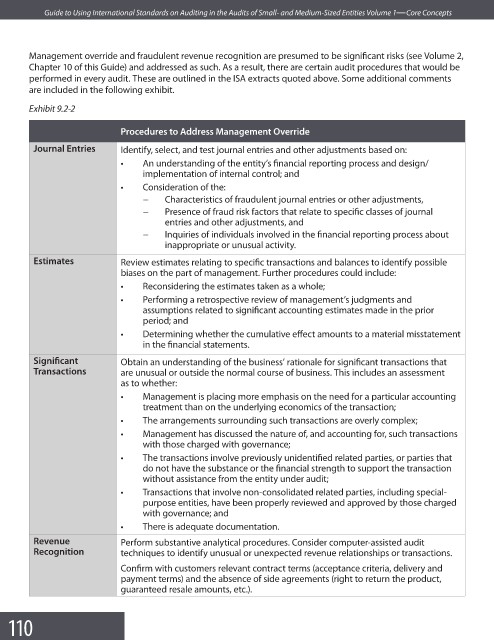
Exhibit 9.2-2
Procedures to Address Management Override
Journal Entries Identify, select, and test journal entries and other adjustments based on:
• An understanding of the entity’s financial reporting process and design/
implementation of internal control; and
• Consideration of the:
− Characteristics of fraudulent journal entries or other adjustments,
− Presence of fraud risk factors that relate to specific classes of journal
entries and other adjustments, and
− Inquiries of individuals involved in the financial reporting process about
inappropriate or unusual activity.
Estimates Review estimates relating to specific transactions and balances to identify possible
biases on the part of management. Further procedures could include:
• Reconsidering the estimates taken as a whole;
• Performing a retrospective review of management’s judgments and
assumptions related to significant accounting estimates made in the prior
period; and
• Determining whether the cumulative effect amounts to a material misstatement
in the fi nancial statements.
Signifi cant Obtain an understanding of the business’ rationale for significant transactions that
Transactions are unusual or outside the normal course of business. This includes an assessment
as to whether:
• Management is placing more emphasis on the need for a particular accounting
treatment than on the underlying economics of the transaction;
• The arrangements surrounding such transactions are overly complex;
• Management has discussed the nature of, and accounting for, such transactions
with those charged with governance;
• The transactions involve previously unidentified related parties, or parties that
do not have the substance or the financial strength to support the transaction
without assistance from the entity under audit;
• Transactions that involve non-consolidated related parties, including special-
purpose entities, have been properly reviewed and approved by those charged
with governance; and
• There is adequate documentation.
Revenue Perform substantive analytical procedures. Consider computer-assisted audit
Recognition techniques to identify unusual or unexpected revenue relationships or transactions.
Confirm with customers relevant contract terms (acceptance criteria, delivery and
payment terms) and the absence of side agreements (right to return the product,
guaranteed resale amounts, etc.).
110