Page 114 - Internal Auditing Standards
P. 114
Guide to Using International Standards on Auditing in the Audits of Small- and Medium-Sized Entities Volume 1—Core Concepts
Designing and Performing Further Audit Procedures
The nature, timing, and extent of further audit procedures are based on, and are responsive to, the assessed
risks of material misstatement at the assertion level. This provides a clear linkage between the auditor’s
further audit procedures and the risk assessment.
The first step is to review the information obtained to date that will form the basis for the design of further
audit procedures. This would include:
• The nature and the reasoning for the assessed risks (such as business and fraud risks) at both the
financial- statement and assertion levels;
• The account balances, classes of transactions, or disclosures that are material to the fi nancial statements;
• The need (if any) to perform tests of controls. This would occur where substantive procedures alone
cannot provide sufficient appropriate audit evidence at the assertion level;
• The auditor’s understanding of the control environment and control activities. In particular, have any
relevant internal controls been identified that, if tested, would provide an effective response to the
assessed risks of material misstatement for a particular assertion; and
• The nature and extent of specific audit procedures that may be required by certain ISAs, or by local rules
and regulations.
Based on the information above, the auditor can design the nature and extent of the procedures to be
performed. Some design considerations are addressed below.
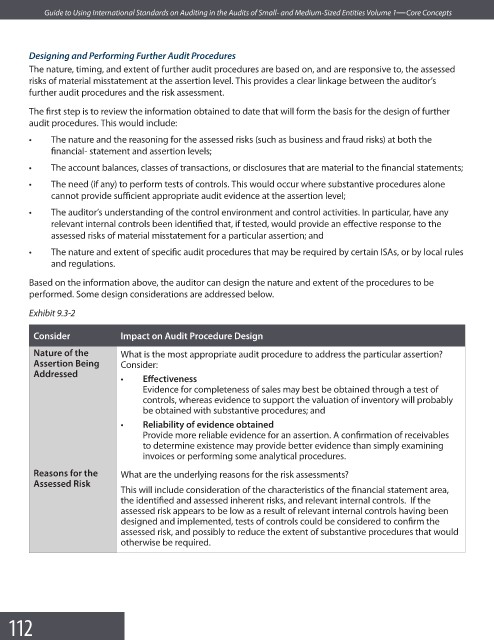
Exhibit 9.3-2
Consider Impact on Audit Procedure Design
Nature of the What is the most appropriate audit procedure to address the particular assertion?
Assertion Being Consider:
Addressed
• Eff ectiveness
Evidence for completeness of sales may best be obtained through a test of
controls, whereas evidence to support the valuation of inventory will probably
be obtained with substantive procedures; and
• Reliability of evidence obtained
Provide more reliable evidence for an assertion. A confirmation of receivables
to determine existence may provide better evidence than simply examining
invoices or performing some analytical procedures.
Reasons for the What are the underlying reasons for the risk assessments?
Assessed Risk
This will include consideration of the characteristics of the financial statement area,
the identified and assessed inherent risks, and relevant internal controls. If the
assessed risk appears to be low as a result of relevant internal controls having been
designed and implemented, tests of controls could be considered to confi rm the
assessed risk, and possibly to reduce the extent of substantive procedures that would
otherwise be required.
112