Page 27 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 27
Evaluation of the Electrocardiogram
and in the cat, the normal MEA is between 0 and left axis deviation includes partial or incomplete
bundle branch block. Note that left ventricular
+160 degrees (Fig. 2.5). An easy way to remember
VetBooks.ir the direction of the normal MEA is to visualize hypertrophy does not usually result in the left
axis shift, as the normal MEA is already pointing
a dorsoventral or ventrodorsal radiograph and
imagine the normal MEA as pointing from the center in the direction of the left ventricular apex. Less
of the heart toward the left ventricular apex. The commonly, mechanical displacement of the heart to
MEA can be within the normal range or to the right either side of the thorax by space-occupying lesions
or left of the normal range. Common causes of right or lung lobe atelectesis can change the MEA.
axis deviation include right ventricular hypertrophy Examples of animals with a left and right axis shift
or right bundle branch block. A common cause of are shown in Figure 2.6.
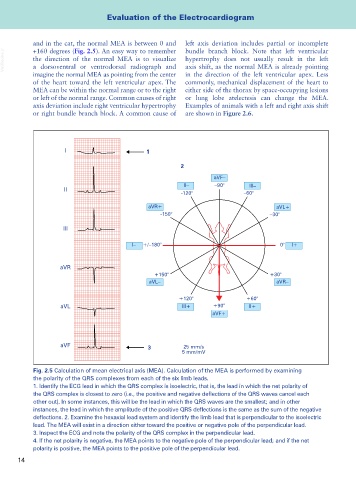
I 1
2
aVF–
II– –90° III–
II
-120° –60°
aVR+ aVL+
-150° –30°
III
I– +/–180° 0° I+
aVR
+150° +30°
aVL– aVR–
+120° +60°
aVL III+ +90° II+
aVF+
aVF 3 25 mm/s
5 mm/mV
Fig. 2.5 Calculation of mean electrical axis (MEA). Calculation of the MEA is performed by examining
the polarity of the QRS complexes from each of the six limb leads.
1. Identify the ECG lead in which the QRS complex is isoelectric, that is, the lead in which the net polarity of
the QRS complex is closest to zero (i.e., the positive and negative deflections of the QRS waves cancel each
other out). In some instances, this will be the lead in which the QRS waves are the smallest; and in other
instances, the lead in which the amplitude of the positive QRS deflections is the same as the sum of the negative
deflections. 2. Examine the hexaxial lead system and identify the limb lead that is perpendicular to the isoelectric
lead. The MEA will exist in a direction either toward the positive or negative pole of the perpendicular lead.
3. Inspect the ECG and note the polarity of the QRS complex in the perpendicular lead.
4. If the net polarity is negative, the MEA points to the negative pole of the perpendicular lead; and if the net
polarity is positive, the MEA points to the positive pole of the perpendicular lead.
14