Page 29 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 29
Evaluation of the Electrocardiogram
WAVEFORM MORPHOLOGY AND The PR interval
INTERVALS
The PR interval represents the time it takes for
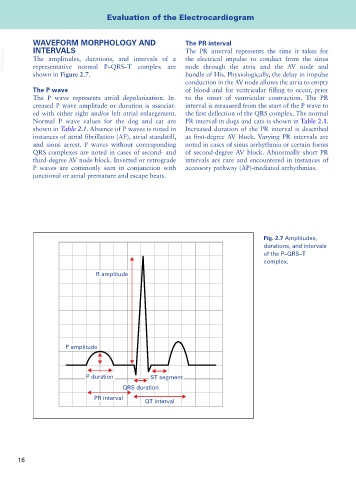
VetBooks.ir The amplitudes, durations, and intervals of a the electrical impulse to conduct from the sinus
node through the atria and the AV node and
representative normal P–QRS–T complex are
shown in Figure 2.7. bundle of His. Physiologically, the delay in impulse
conduction in the AV node allows the atria to empty
The P wave of blood and for ventricular filling to occur, prior
The P wave represents atrial depolarization. In- to the onset of ventricular contraction. The PR
creased P wave amplitude or duration is associat- interval is measured from the start of the P wave to
ed with either right and/or left atrial enlargement. the first deflection of the QRS complex. The normal
Normal P wave values for the dog and cat are PR interval in dogs and cats is shown in Table 2.1.
shown in Table 2.1. Absence of P waves is noted in Increased duration of the PR interval is described
instances of atrial fibrillation (AF), atrial standstill, as first-degree AV block. Varying PR intervals are
and sinus arrest. P waves without corresponding noted in cases of sinus arrhythmia or certain forms
QRS complexes are noted in cases of second- and of second-degree AV block. Abnormally short PR
third-degree AV node block. Inverted or retrograde intervals are rare and encountered in instances of
P waves are commonly seen in conjunction with accessory pathway (AP)-mediated arrhythmias.
junctional or atrial premature and escape beats.
Fig. 2.7 Amplitudes,
durations, and intervals
of the P–QRS–T
complex.
R amplitude
P amplitude
P duration ST segment
QRS duration
PR interval
QT interval
16