Page 33 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 33
Evaluation of the Electrocardiogram
BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK markedly prolonged QRS duration (>0.08 s in the
The bundle of His is specialized conduction tissue
VetBooks.ir that forms the distal portion of the AV node, and dog and >0.06 s in the cat). Examples of RBBB and
divides into two main bundle branches that course
LBBB are shown in Figures 2.10 and 2.11. The
left- and rightward into the ventricular muscle. wide QRS morphology of a bundle branch block
Right (RBBB) or left (LBBB) bundle branch block pattern may be confused with a ventricular rhythm.
occurs when the impulse is blocked or slowed Impulse origin in most cases of bundle branch
within either of the branches and block results in block is the sinus node, hence there is a P wave
characteristic QRS waveform changes. In order associated with each QRS complex and the rhythm
to diagnose a bundle branch block, the MEA has is supraventricular, despite the marked change in
to be determined, which requires a 6-lead ECG QRS waveform morphology. RBBB is typically a
recording. RBBB is characterized by a right shift of benign finding in both dogs and cats, whereas LBBB
the MEA and markedly prolonged QRS duration is usually associated with severe underlying heart
(>0.08 s in the dog and >0.06 s in the cat), while disease.
LBBB is characterized by a normal MEA and
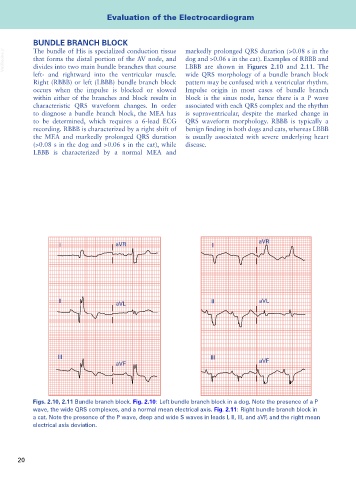
aVR
I aVR I
II aVL II aVL
III III
aVF aVF
Figs. 2.10, 2.11 Bundle branch block. Fig. 2.10: Left bundle branch block in a dog. Note the presence of a P
wave, the wide QRS complexes, and a normal mean electrical axis. Fig. 2.11: Right bundle branch block in
a cat. Note the presence of the P wave, deep and wide S waves in leads I, II, III, and aVF, and the right mean
electrical axis deviation.
20