Page 35 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 35
Approach to Evaluating Arrhythmias
HOW DOES ONE DIFFERENTIATE
SUPRAVENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS
VetBooks.ir FROM VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS? Ventricular arrhythmias: General criteria (Fig. 3.3):
Supraventricular arrhythmias: General criteria
(Fig. 3.2): • Wide QRS complex.
• Ectopic beats display a narrow QRS complex. • Morphology of ectopic QRS complexes and
• Morphology of ectopic QRS complexes and sinus beat QRS complexes are dissimilar.
sinus beat QRS complexes are similar. • P waves are not associated with the ectopic QRS
• P waves usually associated with the ectopic QRS complex.
(unless heart rate is rapid enough so that the P • If fusion beats are present, this supports a
waves are buried within the preceding T wave diagnosis of ventricular ectopic complexes.
or if AF or atrial flutter [AFL] are present).
• P wave morphology of ectopic beats can appear
different from the sinus P wave.
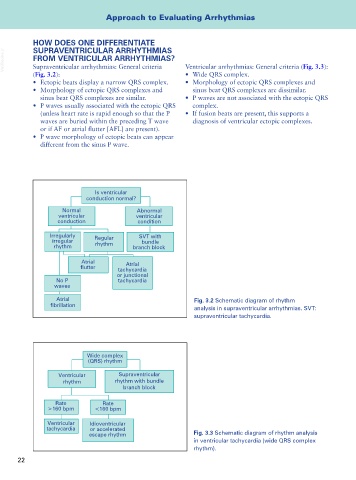
Is ventricular
conduction normal?
Normal Abnormal
ventricular ventricular
conduction condition
Irregularly Regular SVT with
irregular bundle
rhythm rhythm branch block
Atrial Atrial
tachycardia
or junctional
No P tachycardia
waves
Atrial Fig. 3.2 Schematic diagram of rhythm
analysis in supraventricular arrhythmias. SVT:
supraventricular tachycardia.
Wide complex
(QRS) rhythm
Ventricular Supraventricular
rhythm rhythm with bundle
branch block
Rate Rate
>160 bpm <160 bpm
Ventricular Idioventricular
tachycardia or accelerated
escape rhythm Fig. 3.3 Schematic diagram of rhythm analysis
in ventricular tachycardia (wide QRS complex
rhythm).
22