Page 34 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 34
Section 3
VetBooks.ir APPROACH TO
EVALUATING
ARRHYTHMIAS
Cardiac arrhythmias are defined as variations SYSTEMIC APPROACH TO RHYTHM
of the cardiac rhythm from normal sinus rhythm DIAGNOSIS
(too rapid, too slow, or too irregular). “Ectopic” Questions to ask:
beats are those that arise from a source other than • Is the rate fast or slow (tachycardia vs.
the sinus node. Some cardiac arrhythmias are bradycardia)?
benign and clinically insignificant and require no • Is the rhythm regular or irregular? If irregular, is
therapy, whereas other arrhythmias are malignant the rate slow, fast, or are there premature beats?
and potentially life-threatening (i.e., ventricular • Are there P waves? Are they normal (upright in
tachycardia [VT] or ventricular fibrillation [VF]) lead II – i.e., is the rhythm sinus or not sinus)
causing clinical signs such as weakness, lethargy, (Fig. 3.1)?
syncope, or sudden death. • Is there a P wave for every QRS; is there a QRS
Although a specific diagnosis may be suggested for every P wave?
by auscultation (i.e., AF, high-grade AV block) and • Are the QRS complexes normal or abnormal
physical examination, an ECG is required for a (normal or abnormal conduction)?
definitive diagnosis.
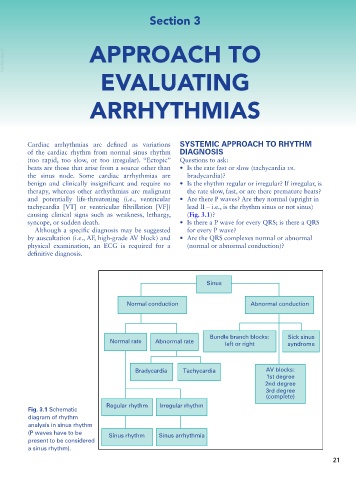
Sinus
Normal conduction Abnormal conduction
Bundle branch blocks: Sick sinus
Normal rate Abnormal rate left or right syndrome
Bradycardia Tachycardia AV blocks:
1st degree
2nd degree
3rd degree
(complete)
Regular rhythm Irregular rhythm
Fig. 3.1 Schematic
diagram of rhythm
analysis in sinus rhythm
(P waves have to be Sinus rhythm Sinus arrhythmia
present to be considered
a sinus rhythm).
21