Page 435 - Feline Cardiology
P. 435
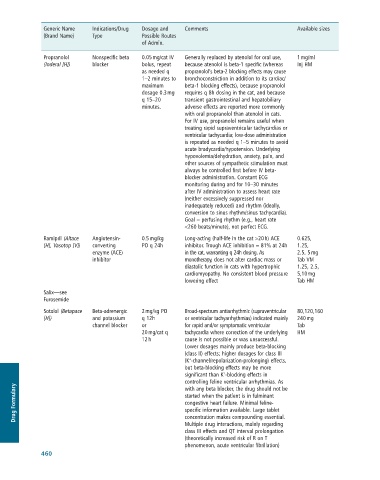
Generic Name Indications/Drug Dosage and Comments Available sizes
(Brand Name) Type Possible Routes
of Admin.
Propranolol Nonspecific beta 0.05 mg/cat IV Generally replaced by atenolol for oral use, 1 mg/ml
(Inderal [H]) blocker bolus, repeat because atenolol is beta-1 specific (whereas Inj HM
as needed q propranolol’s beta-2 blocking effects may cause
1–2 minutes to bronchoconstriction in addition to its cardiac/
maximum beta-1 blocking effects), because propranolol
dosage 0.3 mg requires q 8h dosing in the cat, and because
q 15–20 transient gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary
minutes. adverse effects are reported more commonly
with oral propranolol than atenolol in cats.
For IV use, propranolol remains useful when
treating rapid supraventricular tachycardias or
ventricular tachycardia; low-dose administration
is repeated as needed q 1–5 minutes to avoid
acute bradycardia/hypotension. Underlying
hypovolemia/dehydration, anxiety, pain, and
other sources of sympathetic stimulation must
always be controlled first before IV beta-
blocker administration. Constant ECG
monitoring during and for 10–30 minutes
after IV administration to assess heart rate
(neither excessively suppressed nor
inadequately reduced) and rhythm (ideally,
conversion to sinus rhythm/sinus tachycardia).
Goal = perfusing rhythm (e.g., heart rate
<260 beats/minute), not perfect ECG.
Ramipril (Altace Angiotensin- 0.5 mg/kg Long-acting (half-life in the cat >20 h) ACE 0.625,
[H], Vasotop [V]) converting PO q 24h inhibitor. Trough ACE inhibition = 81% at 24h 1.25,
enzyme (ACE) in the cat, warranting q 24h dosing. As 2.5, 5 mg
inhibitor monotherapy, does not alter cardiac mass or Tab VM
diastolic function in cats with hypertrophic 1.25, 2.5,
cardiomyopathy. No consistent blood pressure 5,10 mg
lowering effect Tab HM
Salix—see
Furosemide
Sotalol (Betapace Beta-adrenergic 2 mg/kg PO Broad-spectrum antiarrhythmic (supraventricular 80,120,160
[H]) and potassium q 12h or ventricular tachyarrhythmias) indicated mainly 240 mg
channel blocker or for rapid and/or symptomatic ventricular Tab
20 mg/cat q tachycardia where correction of the underlying HM
12 h cause is not possible or was unsuccessful.
Lower dosages mainly produce beta-blocking
(class II) effects; higher dosages for class III
+
(K -channel/repolarization-prolonging) effects,
but beta-blocking effects may be more
+
significant than K -blocking effects in
controlling feline ventricular arrhythmias. As
Drug Formulary started when the patient is in fulminant
with any beta blocker, the drug should not be
congestive heart failure. Minimal feline-
specific information available. Large tablet
concentration makes compounding essential.
Multiple drug interactions, mainly regarding
class III effects and QT interval prolongation
(theoretically increased risk of R on T
phenomenon, acute ventricular fibrillation)
460