Page 574 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 574
Macrocyclic Lactone Endectocides Chapter | 43 541
VetBooks.ir dogs at dosages of 3 μg/kg orally (Interceptor), 17 μg/kg
subcutaneously (sustained-release injection, ProHeart6),
and 2.5 mg/kg topically (Advantage-Multi). In livestock,
moxidectin is used as an oral, injectable and pour-on para-
siticide in dosages ranging from 200 to 1000 μg/kg
(Cydectin, Quest). Moxidectin tolerances for cattle are
900 ppb in fat, 200 ppb in liver, 50 ppb in muscle and
40 ppb in milk; tolerances for sheep are 900 ppb in fat,
200 ppb in liver, and 50 ppb in muscle (CFR, 1998).
As a class, MLs have a wide margin of safety when
used in the appropriate species and at appropriate
dosages. Toxicoses generally occur due to accidental or
intentional overdoses or when products are misused, such
as using a livestock formulation in a small companion
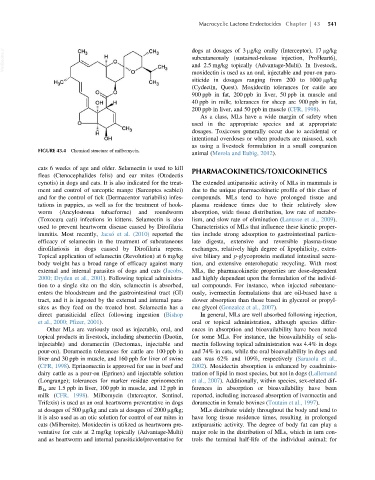
FIGURE 43.4 Chemical structure of milbemycin.
animal (Merola and Eubig, 2012).
cats 6 weeks of age and older. Selamectin is used to kill PHARMACOKINETICS/TOXICOKINETICS
fleas (Ctenocephalides felis) and ear mites (Otodectis
cynotis) in dogs and cats. It is also indicated for the treat- The extended antiparasitic activity of MLs in mammals is
ment and control of sarcoptic mange (Sarcoptes scabiei) due to the unique pharmacokinetic profile of this class of
and for the control of tick (Dermacentor variabilis) infes- compounds. MLs tend to have prolonged tissue and
tations in puppies, as well as for the treatment of hook- plasma residence times due to their relatively slow
worm (Ancylostoma tubaeforme) and roundworm absorption, wide tissue distribution, low rate of metabo-
(Toxocara cati) infections in kittens. Selamectin is also lism, and slow rate of elimination (Lanusse et al., 2009).
used to prevent heartworm disease caused by Dirofilaria Characteristics of MLs that influence these kinetic proper-
immitis. Most recently, Jacso ´ et al. (2010) reported the ties include strong adsorption to gastrointestinal particu-
efficacy of selamectin in the treatment of subcutaneous late digesta, extensive and reversible plasma-tissue
dirofilariosis in dogs caused by Dirofilaria repens. exchanges, relatively high degree of lipophilicity, exten-
Topical application of selamectin (Revolution) at 6 mg/kg sive biliary and p-glycoprotein mediated intestinal secre-
body weight has a broad range of efficacy against many tion, and extensive enterohepatic recycling. With most
external and internal parasites of dogs and cats (Jacobs, MLs, the pharmacokinetic properties are dose-dependent
2000; Dryden et al., 2001). Following topical administra- and highly dependent upon the formulation of the individ-
tion to a single site on the skin, selamectin is absorbed, ual compounds. For instance, when injected subcutane-
enters the bloodstream and the gastrointestinal tract (GI) ously, ivermectin formulations that are oil-based have a
tract, and it is ingested by the external and internal para- slower absorption than those based in glycerol or propyl-
sites as they feed on the treated host. Selamectin has a ene glycol (Gonzalez et al., 2007).
direct parasiticidal effect following ingestion (Bishop In general, MLs are well absorbed following injection,
et al., 2000; Pfizer, 2001). oral or topical administration, although species differ-
Other MLs are variously used as injectable, oral, and ences in absorption and bioavailability have been noted
topical products in livestock, including abamectin (Duotin, for some MLs. For instance, the bioavailability of sela-
injectable) and doramectin (Dectomax, injectable and mectin following topical administration was 4.4% in dogs
pour-on). Doramectin tolerances for cattle are 100 ppb in and 74% in cats, while the oral bioavailability in dogs and
liver and 30 ppb in muscle, and 160 ppb for liver of swine cats was 62% and 109%, respectively (Sarasola et al.,
(CFR, 1998). Eprinomectin is approved for use in beef and 2002). Moxidectin absorption is enhanced by coadminis-
dairy cattle as a pour-on (Eprinex) and injectable solution tration of lipid in most species, but not in dogs (Lallemand
(Longrange); tolerances for marker residue eprinomectin et al., 2007). Additionally, within species, sex-related dif-
B 1a are 1.5 ppb in liver, 100 ppb in muscle, and 12 ppb in ferences in absorption or bioavailability have been
milk (CFR, 1998). Milbemycin (Interceptor, Sentinel, reported, including increased absorption of ivermectin and
Trifexis) is used as an oral heartworm preventative in dogs doramectin in female bovines (Toutain et al., 1997).
at dosages of 500 μg/kg and cats at dosages of 2000 μg/kg; MLs distribute widely throughout the body and tend to
it is also used as an otic solution for control of ear mites in have long tissue residence times, resulting in prolonged
cats (Milbemite). Moxidectin is utilized as heartworm pre- antiparasitic activity. The degree of body fat can play a
ventative for cats at 2 mg/kg topically (Advantage-Multi) major role in the distribution of MLs, which in turn con-
and as heartworm and internal parasiticide/preventative for trols the terminal half-life of the individual animal; for