Page 123 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 123
7.2 Comauted Tomograahy and agnetic Resonance maging 121
A P P
C
A I
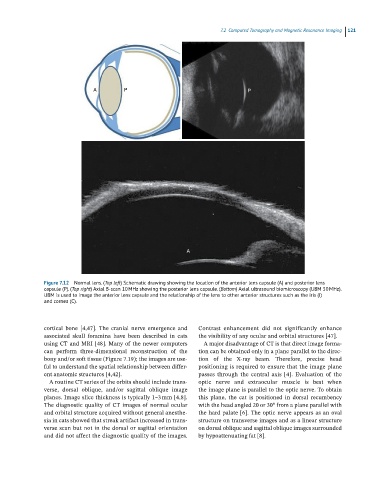
Figure 7.12 Normal lens. (Top left) Schematic drawing showing the location of the anterior lens capsule (A) and posterior lens
capsule (P). (Toa right) Axial B-scan 10 MHz showing the posterior lens capsule. (Bottom) Axial ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM 50 MHz).
UBM is used to image the anterior lens capsule and the relationship of the lens to other anterior structures such as the iris (I)
and cornea (C).
cortical bone [4,47]. The cranial nerve emergence and Contrast enhancement did not significantly enhance
associated skull foramina have been described in cats the visibility of any ocular and orbital structures [47].
using CT and MRI [48]. Many of the newer computers A major disadvantage of CT is that direct image forma-
can perform three‐dimensional reconstruction of the tion can be obtained only in a plane parallel to the direc-
bony and/or soft tissue (Figure 7.19); the images are use - tion of the X‐ray beam. Therefore, precise head
ful to understand the spatial relationship between differ- positioning is required to ensure that the image plane
ent anatomic structures [4,42]. passes through the central axis [4]. Evaluation of the
A routine CT series of the orbits should include trans - optic nerve and extraocular muscle is best when
verse, dorsal oblique, and/or sagittal oblique image the image plane is parallel to the optic nerve. To obtain
planes. Image slice thickness is typically 1–3 mm [4,8]. this plane, the cat is positioned in dorsal recumbency
The diagnostic quality of CT images of normal ocular with the head angled 20 or 30° from a plane parallel with
and orbital structure acquired without general anesthe - the hard palate [6]. The optic nerve appears as an oval
sia in cats showed that streak artifact increased in trans - structure on transverse images and as a linear structure
verse scan but not in the dorsal or sagittal orientation on dorsal oblique and sagittal oblique images surrounded
and did not affect the diagnostic quality of the images. by hypoattenuating fat [8].