Page 124 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 124
122 7 Normal Cross-sectional Anatomy of the Eye and Orbit
Cornea
Iris
Anterior lens
capsule
Figure 7.13 Normal iris. (Left) Schematic drawing showing the relationship between the anterior lens capsule and iris. (Right) UBM
image; the iris appears as a bright interface on the surface of the anterior lens capsule.
DLCP
AOD
CP
Figure 7.14 Normal ciliary body. Ultrasound biomicroscopy
50 MHz images demonstrating the normal appearance of
ciliary processes in cats. CC, ciliary cleft; CP, ciliary processes; I,
iris; S, sclera.
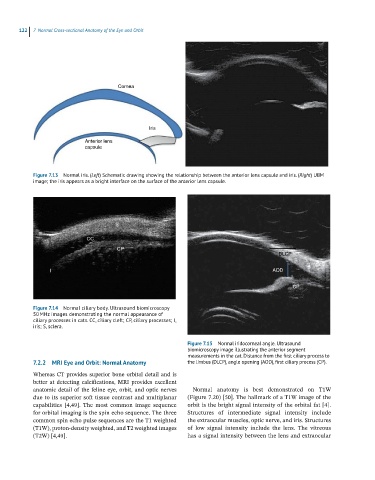
Figure 7.15 Normal iridocorneal angle. Ultrasound
biomicroscopy image illustrating the anterior segment
measurements in the cat. Distance from the first ciliary process to
7.2.2 MRI Eye and Orbit: Normal Anatomy the limbus (DLCP), angle opening (AOD), first ciliary process (CP).
Whereas CT provides superior bone orbital detail and is
better at detecting calcifications, MRI provides excellent
anatomic detail of the feline eye, orbit, and optic nerves Normal anatomy is best demonstrated on T1W
due to its superior soft tissue contrast and multiplanar (Figure 7.20) [50]. The hallmark of a T1W image of the
capabilities [4,49]. The most common image sequence orbit is the bright signal intensity of the orbital fat [4].
for orbital imaging is the spin echo sequence. The three Structures of intermediate signal intensity include
common spin echo pulse sequences are the T1 weighted the extraocular muscles, optic nerve, and iris. Structures
(T1W), proton‐density weighted, and T2 weighted images of low signal intensity include the lens. The vitreous
(T2W) [4,49]. has a signal intensity between the lens and extraocular