Page 131 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 131
130 8 Diseases of the Eye
(a) (b) (c)
L L L
V V
C
I
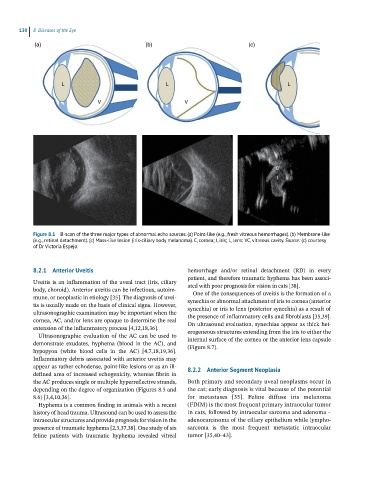
Figure 8.1 B-scan of the three major types of abnormal echo sources. (a) Point-like (e.g., fresh vitreous hemorrhages). (b) Membrane-like
(e.g., retinal detachment). (c) Mass-like lesion (iris-ciliary body melanoma). C, cornea; I, iris; L, lens; VC, vitreous cavity. Source: (c) courtesy
of Dr Victoria Espejo.
8.2.1 Anterior Uveitis hemorrhage and/or retinal detachment (RD) in every
patient, and therefore traumatic hyphema has been associ-
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uveal tract (iris, ciliary ated with poor prognosis for vision in cats [38].
body, choroid). Anterior uveitis can be infectious, autoim- One of the consequences of uveitis is the formation of a
mune, or neoplastic in etiology [35]. The diagnosis of uvei- synechia or abnormal attachment of iris to cornea (anterior
tis is usually made on the basis of clinical signs. However, synechia) or iris to lens (posterior synechia) as a result of
ultrasonographic examination may be important when the the presence of inflammatory cells and fibroblasts [35,39].
cornea, AC, and/or lens are opaque to determine the real On ultrasound evaluation, synechiae appear as thick het-
extension of the inflammatory process [4,12,18,36]. erogeneous structures extending from the iris to either the
Ultrasonographic evaluation of the AC can be used to internal surface of the cornea or the anterior lens capsule
demonstrate exudates, hyphema (blood in the AC), and (Figure 8.7).
hypopyon (white blood cells in the AC) [4,7,18,19,36].
Inflammatory debris associated with anterior uveitis may
appear as rather echodense, point‐like lesions or as an ill‐ 8.2.2 Anterior Segment Neoplasia
defined area of increased echogenicity, whereas fibrin in
the AC produces single or multiple hyperreflective strands, Both primary and secondary uveal neoplasms occur in
depending on the degree of organization (Figures 8.5 and the cat; early diagnosis is vital because of the potential
8.6) [3,4,10,36]. for metastases [35]. Feline diffuse iris melanoma
Hyphema is a common finding in animals with a recent (FDIM) is the most frequent primary intraocular tumor
history of head trauma. Ultrasound can be used to assess the in cats, followed by intraocular sarcoma and adenoma –
intraocular structures and provide prognosis for vision in the adenocarcinoma of the ciliary epithelium while lympho-
presence of traumatic hyphema [2,3,37,38]. One study of six sarcoma is the most frequent metastatic intraocular
feline patients with traumatic hyphema revealed vitreal tumor [35,40–43].