Page 133 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 133
132 8 Diseases of the Eye
(a) (b)
S
C
(c) (d)
S
C
S
C
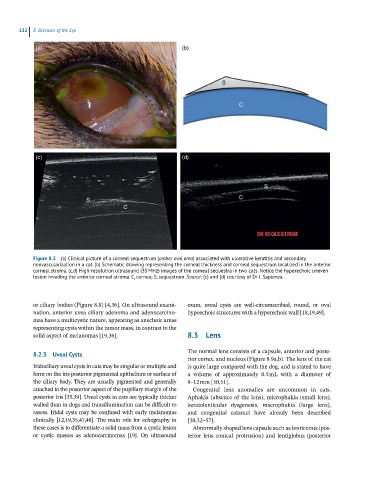
Figure 8.3 (a) Clinical picture of a corneal sequestrum (amber oval area) associated with ulcerative keratitis and secondary
neovascularization in a cat. (b) Schematic drawing representing the corneal thickness and corneal sequestrum localized in the anterior
corneal stroma. (c,d) High-resolution ultrasound (35 MHz) images of the corneal sequestra in two cats. Notice the hyperechoic uneven
lesion invading the anterior corneal stroma. C, cornea; S, sequestrum. Source: (c) and (d) courtesy of Dr J. Sapienza.
or ciliary bodies (Figure 8.8) [4,36]. On ultrasound exami- exam, uveal cysts are well‐circumscribed, round, or oval
nation, anterior uvea ciliary adenoma and adenocarcino- hypoechoic structures with a hyperechoic wall [18,19,49].
mas have a multicystic nature, appearing as anechoic areas
representing cysts within the tumor mass, in contrast to the
solid aspect of melanomas [19,36]. 8.3 Lens
The normal lens consists of a capsule, anterior and poste-
8.2.3 Uveal Cysts
rior cortex, and nucleus (Figure 8.9a,b). The lens of the cat
Iridociliary uveal cysts in cats may be singular or multiple and is quite large compared with the dog, and is stated to have
form on the iris posterior pigmented epithelium or surface of a volume of approximately 0.5 mL with a diameter of
the ciliary body. They are usually pigmented and generally 9–12 mm [50,51].
attached to the posterior aspect of the pupillary margin of the Congenital lens anomalies are uncommon in cats.
posterior iris [35,39]. Uveal cysts in cats are typically thicker Aphakia (absence of the lens), microphakia (small lens),
walled than in dogs and transillumination can be difficult to keratolenticular dysgenesis, macrophakia (large lens),
assess. Iridal cysts may be confused with early melanomas and congenital cataract have already been described
clinically [12,19,35,47,48]. The main role for echography in [50,52–57].
these cases is to differentiate a solid mass from a cystic lesion Abnormally shaped lens capsule such as lenticonus (pos-
or cystic masses as adenocarcinomas [19]. On ultrasound terior lens conical protrusion) and lentiglobus (posterior