Page 136 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 136
8.3 ens 135
(a) (b)
CB
I
(c) (d)
C
I C
I
AC L
AC
L
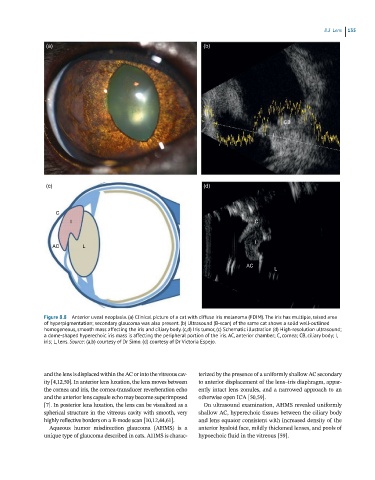
Figure 8.8 Anterior uveal neoplasia. (a) Clinical picture of a cat with diffuse iris melanoma (FDIM). The iris has multiple, raised area
of hyperpigmentation; secondary glaucoma was also present. (b) Ultrasound (B-scan) of the same cat shows a solid well-outlined
homogeneous, smooth mass affecting the iris and ciliary body. (c,d) Iris tumor, (c) Schematic illustration (d) High-resolution ultrasound;
a dome-shaped hyperechoic iris mass is affecting the peripheral portion of the iris. AC, anterior chamber; C, cornea; CB, ciliary body; I,
iris; L, lens. Source: (a,b) courtesy of Dr Simo. (d) courtesy of Dr Victoria Espejo.
and the lens is displaced within the AC or into the vitreous cav - terized by the presence of a uniformly shallow AC secondary
ity [4,12,50]. In anterior lens luxation, the lens moves between to anterior displacement of the lens–iris diaphragm, appar-
the cornea and iris, the cornea‐transducer reverberation echo ently intact lens zonules, and a narrowed approach to an
and the anterior lens capsule echo may become superimposed otherwise open ICA [50,59].
[7]. In posterior lens luxation, the lens can be visualized as a On ultrasound examination, AHMS revealed uniformly
spherical structure in the vitreous cavity with smooth, very shallow AC, hyperechoic tissues between the ciliary body
highly reflective borders on a B‐mode scan [10,12,44,61]. and lens equator consistent with increased density of the
Aqueous humor misdirection glaucoma (AHMS) is a anterior hyaloid face, mildly thickened lenses, and pools of
unique type of glaucoma described in cats. AHMS is charac- hypoechoic fluid in the vitreous [59].