Page 140 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 140
8.4 Vitreous 139
(a) (b)
AC
L
V
(c) (d)
AC
L V
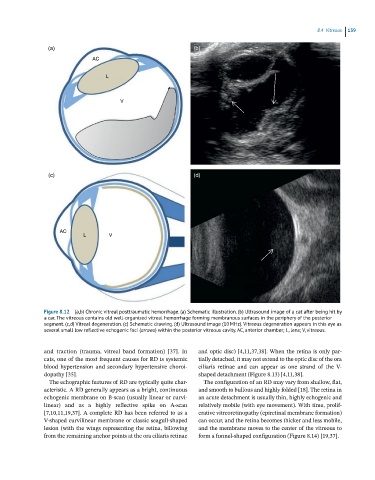
Figure 8.12 (a,b) Chronic vitreal posttraumatic hemorrhage. (a) Schematic illustration. (b) Ultrasound image of a cat after being hit by
a car. The vitreous contains old well-organized vitreal hemorrhage forming membranous surfaces in the periphery of the posterior
segment. (c,d) Vitreal degeneration. (c) Schematic drawing. (d) Ultrasound image (10 MHz). Vitreous degeneration appears in this eye as
several small low reflective echogenic foci (arrows) within the posterior vitreous cavity. AC, anterior chamber; L, lens; V, vitreous.
and traction (trauma, vitreal band formation) [37]. In and optic disc) [4,11,37,38]. When the retina is only par-
cats, one of the most frequent causes for RD is systemic tially detached, it may not extend to the optic disc of the ora
blood hypertension and secondary hypertensive choroi- ciliaris retinae and can appear as one strand of the V‐
dopathy [35]. shaped detachment (Figure 8.13) [4,11,38].
The echographic features of RD are typically quite char- The configuration of an RD may vary from shallow, flat,
acteristic. A RD generally appears as a bright, continuous and smooth to bullous and highly folded [18]. The retina in
echogenic membrane on B‐scan (usually linear or curvi- an acute detachment is usually thin, highly echogenic and
linear) and as a highly reflective spike on A‐scan relatively mobile (with eye movement). With time, prolif-
[7,10,11,19,37]. A complete RD has been referred to as a erative vitreoretinopathy (epiretinal membrane formation)
V‐shaped curvilinear membrane or classic seagull‐shaped can occur, and the retina becomes thicker and less mobile,
lesion (with the wings representing the retina, billowing and the membrane moves to the center of the vitreous to
from the remaining anchor points at the ora ciliaris retinae form a funnel‐shaped configuration (Figure 8.14) [19,37].