Page 139 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 139
138 8 Diseases of the Eye
(a) (b)
C
AC AC
L C
L C
I
L N
L N
(c) (d)
L
L
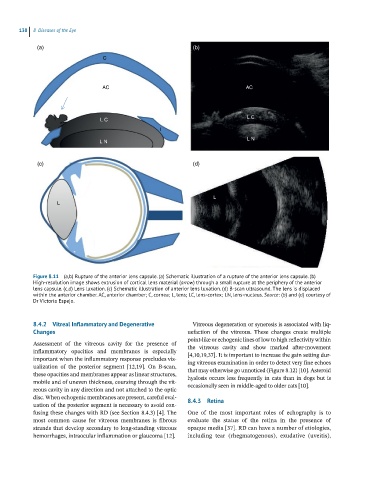
Figure 8.11 (a,b) Rupture of the anterior lens capsule. (a) Schematic illustration of a rupture of the anterior lens capsule. (b)
High-resolution image shows extrusion of cortical lens material (arrow) through a small rupture at the periphery of the anterior
lens capsule. (c,d) Lens luxation. (c) Schematic illustration of anterior lens luxation. (d) B-scan ultrasound. The lens is displaced
within the anterior chamber. AC, anterior chamber; C, cornea; L, lens; LC, lens-cortex; LN, lens-nucleus. Source: (b) and (d) courtesy of
Dr Victoria Espejo.
8.4.2 Vitreal Inflammatory and Degenerative Vitreous degeneration or syneresis is associated with liq-
Changes uefaction of the vitreous. These changes create multiple
point‐like or echogenic lines of low to high reflectivity within
Assessment of the vitreous cavity for the presence of the vitreous cavity and show marked after‐movement
inflammatory opacities and membranes is especially [4,10,19,37]. It is important to increase the gain setting dur-
important when the inflammatory response precludes vis- ing vitreous examination in order to detect very fine echoes
ualization of the posterior segment [12,19]. On B‐scan, that may otherwise go unnoticed (Figure 8.12) [10]. Asteroid
these opacities and membranes appear as linear structures, hyalosis occurs less frequently in cats than in dogs but is
mobile and of uneven thickness, coursing through the vit- occasionally seen in middle‐aged to older cats [10].
reous cavity in any direction and not attached to the optic
disc. When echogenic membranes are present, careful eval- 8.4.3 Retina
uation of the posterior segment is necessary to avoid con-
fusing these changes with RD (see Section 8.4.3) [4]. The One of the most important roles of echography is to
most common cause for vitreous membranes is fibrous evaluate the status of the retina in the presence of
strands that develop secondary to long‐standing vitreous opaque media [37]. RD can have a number of etiologies,
hemorrhages, intraocular inflammation or glaucoma [12]. including tear (rhegmatogenous), exudative (uveitis),