Page 182 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 182
184 11 Advanced Imaging Modalities
(a) (b)
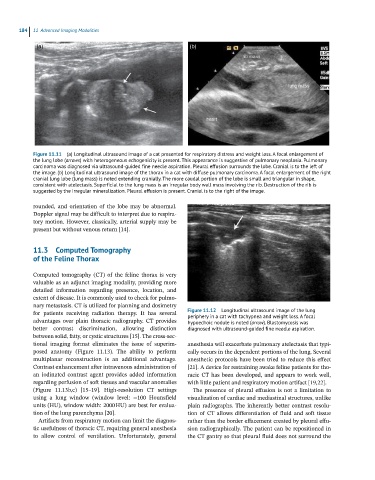
Figure 11.11 (a) Longitudinal ultrasound image of a cat presented for respiratory distress and weight loss. A focal enlargement of
the lung lobe (arrows) with heterogeneous echogenicity is present. This appearance is suggestive of pulmonary neoplasia. Pulmonary
carcinoma was diagnosed via ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. Pleural effusion surrounds the lobe. Cranial is to the left of
the image. (b) Longitudinal ultrasound image of the thorax in a cat with diffuse pulmonary carcinoma. A focal enlargement of the right
cranial lung lobe (lung mass) is noted extending cranially. The more caudal portion of the lobe is small and triangular in shape,
consistent with atelectasis. Superficial to the lung mass is an irregular body wall mass involving the rib. Destruction of the rib is
suggested by the irregular mineralization. Pleural effusion is present. Cranial is to the right of the image.
rounded, and orientation of the lobe may be abnormal.
Doppler signal may be difficult to interpret due to respira-
tory motion. However, classically, arterial supply may be
present but without venous return [14].
11.3 Computed Tomography
of the Feline Thorax
Computed tomography (CT) of the feline thorax is very
valuable as an adjunct imaging modality, providing more
detailed information regarding presence, location, and
extent of disease. It is commonly used to check for pulmo-
nary metastasis. CT is utilized for planning and dosimetry
for patients receiving radiation therapy. It has several Figure 11.12 Longitudinal ultrasound image of the lung
periphery in a cat with tachypnea and weight loss. A focal
advantages over plain thoracic radiography. CT provides hypoechoic nodule is noted (arrow). Blastomycosis was
better contrast discrimination, allowing distinction diagnosed with ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration.
between solid, fatty, or cystic structures [15]. The cross‐sec-
tional imaging format eliminates the issue of superim- anesthesia will exacerbate pulmonary atelectasis that typi-
posed anatomy (Figure 11.13). The ability to perform cally occurs in the dependent portions of the lung. Several
multiplanar reconstruction is an additional advantage. anesthetic protocols have been tried to reduce this effect
Contrast enhancement after intravenous administration of [21]. A device for restraining awake feline patients for tho-
an iodinated contrast agent provides added information racic CT has been developed, and appears to work well,
regarding perfusion of soft tissues and vascular anomalies with little patient and respiratory motion artifact [19,22].
(Figure 11.13b,c) [15–19]. High‐resolution CT settings The presence of pleural effusion is not a limitation to
using a lung window (window level: −100 Hounsfield visualization of cardiac and mediastinal structures, unlike
units (HU), window width: 2000 HU) are best for evalua- plain radiographs. The inherently better contrast resolu-
tion of the lung parenchyma [20]. tion of CT allows differentiation of fluid and soft tissue
Artifacts from respiratory motion can limit the diagnos- rather than the border effacement created by pleural effu-
tic usefulness of thoracic CT, requiring general anesthesia sion radiographically. The patient can be repositioned in
to allow control of ventilation. Unfortunately, general the CT gantry so that pleural fluid does not surround the