Page 183 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 183
11.3 Computed CoCogrmphy Cofuptf telit pCgra 185
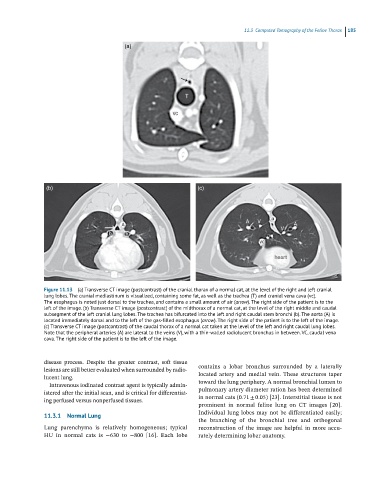
(a)
(b) (c)
Figure 11.13 (a) Transverse CT image (postcontrast) of the cranial thorax of a normal cat, at the level of the right and left cranial
lung lobes. The cranial mediastinum is visualized, containing some fat, as well as the trachea (T) and cranial vena cava (vc).
The esophagus is noted just dorsal to the trachea, and contains a small amount of air (arrow). The right side of the patient is to the
left of the image. (b) Transverse CT image (postcontrast) of the midthorax of a normal cat, at the level of the right middle and caudal
subsegment of the left cranial lung lobes. The trachea has bifurcated into the left and right caudal stem bronchi (b). The aorta (A) is
located immediately dorsal and to the left of the gas-filled esophagus (arrow). The right side of the patient is to the left of the image.
(c) Transverse CT image (postcontrast) of the caudal thorax of a normal cat taken at the level of the left and right caudal lung lobes.
Note that the peripheral arteries (A) are lateral to the veins (V), with a thin-walled radiolucent bronchus in between. VC, caudal vena
cava. The right side of the patient is to the left of the image.
disease process. Despite the greater contrast, soft tissue
lesions are still better evaluated when surrounded by radio- contains a lobar bronchus surrounded by a laterally
lucent lung. located artery and medial vein. These structures taper
Intravenous iodinated contrast agent is typically admin- toward the lung periphery. A normal bronchial lumen to
istered after the initial scan, and is critical for differentiat- pulmonary artery diameter ration has been determined
ing perfused versus nonperfused tissues. in normal cats (0.71 ± 0.05) [23]. Interstitial tissue is not
prominent in normal feline lung on CT images [20].
11.3.1 Normal Lung Individual lung lobes may not be differentiated easily;
the branching of the bronchial tree and orthogonal
Lung parenchyma is relatively homogeneous; typical reconstruction of the image are helpful in more accu-
HU in normal cats is −630 to −800 [16]. Each lobe rately determining lobar anatomy.