Page 362 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 362
370 22 Gastrointestinal Disease
(a)
(b) (c)
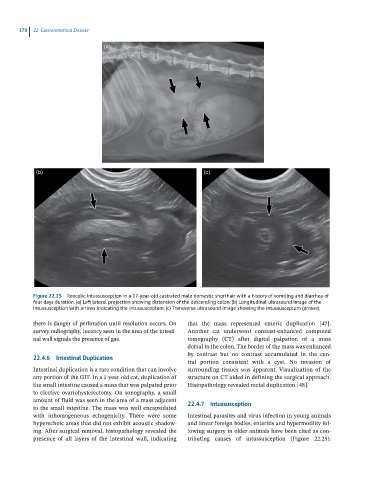
Figure 22.25 Ileocolic intussusception in a 17-year-old castrated male domestic shorthair with a history of vomiting and diarrhea of
four days duration. (a) Left lateral projection showing distension of the descending colon. (b) Longitudinal ultrasound image of the
intussusception with arrows indicating the intussusceptum. (c) Transverse ultrasound image showing the intussusceptum (arrows).
there is danger of perforation until resolution occurs. On that the mass represented enteric duplication [47].
survey radiography, lucency seen in the area of the intesti- Another cat underwent contrast‐enhanced computed
nal wall signals the presence of gas. tomography (CT) after digital palpation of a mass
dorsal to the colon. The border of the mass was enhanced
by contrast but no contrast accumulated in the cen-
22.4.6 Intestinal Duplication
tral portion consistent with a cyst. No invasion of
Intestinal duplication is a rare condition that can involve surrounding tissues was apparent. Visualization of the
any portion of the GIT. In a 1‐year‐old cat, duplication of structure on CT aided in defining the surgical approach.
the small intestine caused a mass that was palpated prior Histopathology revealed rectal duplication [48].
to elective ovariohysterectomy. On sonography, a small
amount of fluid was seen in the area of a mass adjacent 22.4.7 Intussusception
to the small intestine. The mass was well encapsulated
with inhomogeneous echogenicity. There were some Intestinal parasites and virus infection in young animals
hyperechoic areas that did not exhibit acoustic shadow- and linear foreign bodies, enteritis and hypermotility fol-
ing. After surgical removal, histopathology revealed the lowing surgery in older animals have been cited as con-
presence of all layers of the intestinal wall, indicating tributing causes of intussusception (Figure 22.25).