Page 441 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 441
452 26 Normal Urinary System
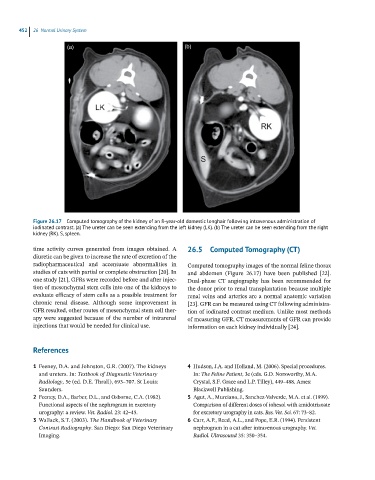
(a) (b)
Figure 26.17 Computed tomography of the kidney of an 8-year-old domestic longhair following intravenous administration of
iodinated contrast. (a) The ureter can be seen extending from the left kidney (LK). (b) The ureter can be seen extending from the right
kidney (RK). S, spleen.
time activity curves generated from images obtained. A 26.5 Computed Tomography (CT)
diuretic can be given to increase the rate of excretion of the
radiopharmaceutical and accentuate abnormalities in Computed tomography images of the normal feline thorax
studies of cats with partial or complete obstruction [20]. In and abdomen (Figure 26.17) have been published [22].
one study [21], GFRs were recorded before and after injec- Dual‐phase CT angiography has been recommended for
tion of mesenchymal stem cells into one of the kidneys to the donor prior to renal transplantation because multiple
evaluate efficacy of stem cells as a possible treatment for renal veins and arteries are a normal anatomic variation
chronic renal disease. Although some improvement in [23]. GFR can be measured using CT following administra-
GFR resulted, other routes of mesenchymal stem cell ther- tion of iodinated contrast medium. Unlike most methods
apy were suggested because of the number of intrarenal of measuring GFR, CT measurements of GFR can provide
injections that would be needed for clinical use. information on each kidney individually [24].
References
1 Feeney, D.A. and Johnston, G.R. (2007). The kidneys 4 Hudson, J.A. and Holland, M. (2006). Special procedures.
and ureters. In: Textbook of Diagnostic Veterinary In: The Feline Patient, 3e (eds. G.D. Norsworthy, M.A.
Radiology, 5e (ed. D.E. Thrall), 693–707. St Louis: Crystal, S.F. Grace and L.P. Tilley), 449–488. Ames:
Saunders. Blackwell Publishing.
2 Feeney, D.A., Barber, D.L., and Osborne, C.A. (1982). 5 Agut, A., Murciano, J., Sanchez‐Valverde, M.A. et al. (1999).
Functional aspects of the nephrogram in excretory Comparison of different doses of iohexol with amidotrizoate
urography: a review. Vet. Radiol. 23: 42–45. for excretory urography in cats. Res. Vet. Sci. 67: 73–82.
3 Wallack, S.T. (2003). The Handbook of Veterinary 6 Carr, A.P., Reed, A.L., and Pope, E.R. (1994). Persistent
Contrast Radiography. San Diego: San Diego Veterinary nephrogram in a cat after intravenous urography. Vet.
Imaging. Radiol. Ultrasound 35: 350–354.