Page 84 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 84
6.2 iseases oo the Feline rain 81
(a) (b)
(d)
(c)
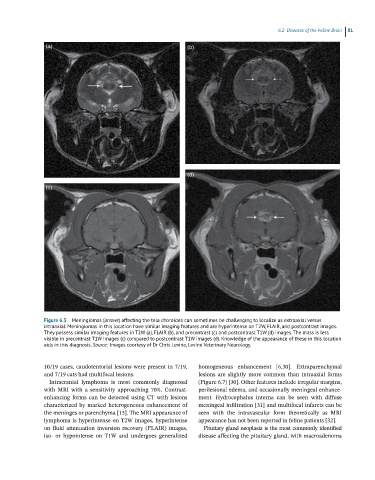
Figure 6.5 Meningiomas (arrows) affecting the tela choroidea can sometimes be challenging to localize as extraaxial versus
intraaxial. Meningiomas in this location have similar imaging features and are hyperintense on T2W, FLAIR, and postcontrast images.
They possess similar imaging features in T2W (a), FLAIR (b), and precontrast (c) and postcontrast T1W (d) images. The mass is less
visible in precontrast T1W images (c) compared to postcontrast T1W images (d). Knowledge of the appearance of these in this location
aids in this diagnosis. Source: Images courtesy of Dr Chris Levine, Levine Veterinary Neurology.
10/19 cases, caudotentorial lesions were present in 7/19, homogeneous enhancement [6,30]. Extraparenchymal
and 7/19 cats had multifocal lesions. lesions are slightly more common than intraaxial forms
Intracranial lymphoma is most commonly diagnosed (Figure 6.7) [30]. Other features include irregular margins,
with MRI with a sensitivity approaching 70%. Contrast‐ perilesional edema, and occasionally meningeal enhance-
enhancing forms can be detected using CT with lesions ment. Hydrocephalus interna can be seen with diffuse
characterized by marked heterogeneous enhancement of meningeal infiltration [31] and multifocal infarcts can be
the meninges or parenchyma [15]. The MRI appearance of seen with the intravascular form theoretically as MRI
lymphoma is hyperintense on T2W images, hyperintense appearance has not been reported in feline patients [32].
on fluid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR) images, Pituitary gland neoplasia is the most commonly identified
iso‐ or hypointense on T1W and undergoes generalized disease affecting the pituitary gland, with macroadenoma