Page 417 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 417
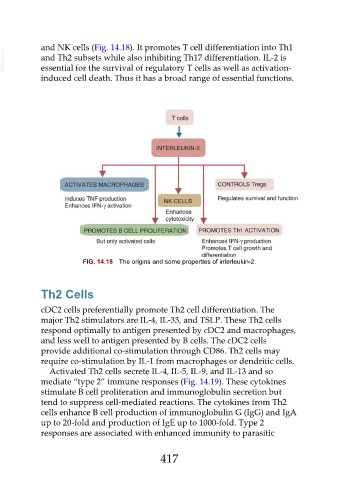
and NK cells (Fig. 14.18). It promotes T cell differentiation into Th1
VetBooks.ir and Th2 subsets while also inhibiting Th17 differentiation. IL-2 is
essential for the survival of regulatory T cells as well as activation-
induced cell death. Thus it has a broad range of essential functions.
FIG. 14.18 The origins and some properties of interleukin-2.
Th2 Cells
cDC2 cells preferentially promote Th2 cell differentiation. The
major Th2 stimulators are IL-4, IL-33, and TSLP. These Th2 cells
respond optimally to antigen presented by cDC2 and macrophages,
and less well to antigen presented by B cells. The cDC2 cells
provide additional co-stimulation through CD86. Th2 cells may
require co-stimulation by IL-1 from macrophages or dendritic cells.
Activated Th2 cells secrete IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, and IL-13 and so
mediate “type 2” immune responses (Fig. 14.19). These cytokines
stimulate B cell proliferation and immunoglobulin secretion but
tend to suppress cell-mediated reactions. The cytokines from Th2
cells enhance B cell production of immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA
up to 20-fold and production of IgE up to 1000-fold. Type 2
responses are associated with enhanced immunity to parasitic
417