Page 419 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 419
VetBooks.ir
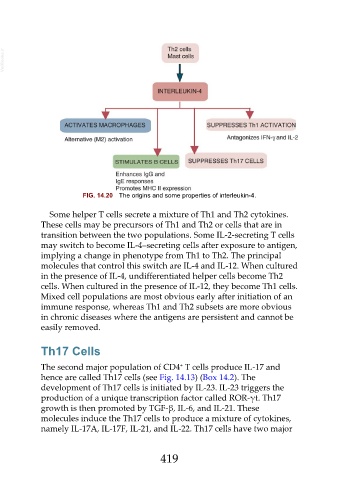
FIG. 14.20 The origins and some properties of interleukin-4.
Some helper T cells secrete a mixture of Th1 and Th2 cytokines.
These cells may be precursors of Th1 and Th2 or cells that are in
transition between the two populations. Some IL-2-secreting T cells
may switch to become IL-4–secreting cells after exposure to antigen,
implying a change in phenotype from Th1 to Th2. The principal
molecules that control this switch are IL-4 and IL-12. When cultured
in the presence of IL-4, undifferentiated helper cells become Th2
cells. When cultured in the presence of IL-12, they become Th1 cells.
Mixed cell populations are most obvious early after initiation of an
immune response, whereas Th1 and Th2 subsets are more obvious
in chronic diseases where the antigens are persistent and cannot be
easily removed.
Th17 Cells
+
The second major population of CD4 T cells produce IL-17 and
hence are called Th17 cells (see Fig. 14.13) (Box 14.2). The
development of Th17 cells is initiated by IL-23. IL-23 triggers the
production of a unique transcription factor called ROR-γt. Th17
growth is then promoted by TGF-β, IL-6, and IL-21. These
molecules induce the Th17 cells to produce a mixture of cytokines,
namely IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21, and IL-22. Th17 cells have two major
419