Page 418 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 418
worms but decreased resistance to mycobacteria and other
VetBooks.ir intracellular organisms. They suppress some autoimmune diseases,
and they neutralize toxins and regulate wound and tissue repair
following infection and injury. When not carefully regulated, type 2
responses may trigger damaging allergic responses.
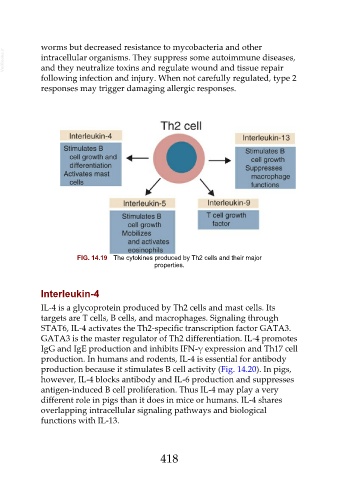
FIG. 14.19 The cytokines produced by Th2 cells and their major
properties.
Interleukin-4
IL-4 is a glycoprotein produced by Th2 cells and mast cells. Its
targets are T cells, B cells, and macrophages. Signaling through
STAT6, IL-4 activates the Th2-specific transcription factor GATA3.
GATA3 is the master regulator of Th2 differentiation. IL-4 promotes
IgG and IgE production and inhibits IFN-γ expression and Th17 cell
production. In humans and rodents, IL-4 is essential for antibody
production because it stimulates B cell activity (Fig. 14.20). In pigs,
however, IL-4 blocks antibody and IL-6 production and suppresses
antigen-induced B cell proliferation. Thus IL-4 may play a very
different role in pigs than it does in mice or humans. IL-4 shares
overlapping intracellular signaling pathways and biological
functions with IL-13.
418