Page 38 - Zoo Animal Learning and Training
P. 38
22 Tasks for the Veterinary Assistant
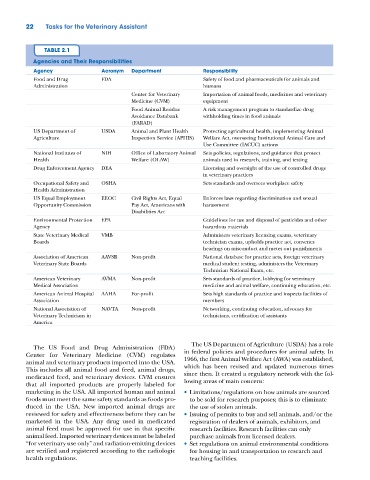
TABLE 2.1
Agencies and Their Responsibilities
Agency Acronym Department Responsibility
Food and Drug FDA Safety of food and pharmaceuticals for animals and
Administration humans
Center for Veterinary Importation of animal foods, medicines and veterinary
Medicine (CVM) equipment
Food Animal Residue A risk management program to standardize drug
Avoidance Databank withholding times in food animals
(FARAD)
US Department of USDA Animal and Plant Health Protecting agricultural health, implementing Animal
Agriculture Inspection Service (APHIS) Welfare Act, overseeing Institutional Animal Care and
Use Committee (IACUC) actions
National Institutes of NIH Office of Laboratory Animal Sets policies, regulations, and guidance that protect
Health Welfare (OLAW) animals used in research, training, and testing
Drug Enforcement Agency DEA Licensing and oversight of the use of controlled drugs
in veterinary practices
Occupational Safety and OSHA Sets standards and oversees workplace safety
Health Administration
US Equal Employment EEOC Civil Rights Act, Equal Enforces laws regarding discrimination and sexual
Opportunity Commission Pay Act, Americans with harassment
Disabilities Act
Environmental Protection EPA Guidelines for use and disposal of pesticides and other
Agency hazardous materials
State Veterinary Medical VMB Administers veterinary licensing exams, veterinary
Boards technician exams, upholds practice act, convenes
hearings on misconduct and metes out punishments
Association of American AAVSB Non‐profit National database for practice acts, foreign veterinary
Veterinary State Boards medical student testing, administers the Veterinary
Technician National Exam, etc.
American Veterinary AVMA Non‐profit Sets standards of practice, lobbying for veterinary
Medical Association medicine and animal welfare, continuing education, etc.
American Animal Hospital AAHA For‐profit Sets high standards of practice and inspects facilities of
Association members
National Association of NAVTA Non‐profit Networking, continuing education, advocacy for
Veterinary Technicians in technicians, certification of assistants
America
The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) has a role
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM) regulates in federal policies and procedures for animal safety. In
1966, the first Animal Welfare Act (AWA) was established,
animal and veterinary products imported into the USA. which has been revised and updated numerous times
This includes all animal food and feed, animal drugs, since then. It created a regulatory network with the fol-
medicated feed, and veterinary devices. CVM ensures lowing areas of main concern:
that all imported products are properly labeled for
marketing in the USA. All imported human and animal • Limitations/regulations on how animals are sourced
foods must meet the same safety standards as foods pro- to be sold for research purposes; this is to eliminate
duced in the USA. New imported animal drugs are the use of stolen animals.
reviewed for safety and effectiveness before they can be • Issuing of permits to buy and sell animals, and/or the
marketed in the USA. Any drug used in medicated registration of dealers of animals, exhibitors, and
animal feed must be approved for use in that specific research facilities. Research facilities can only
animal feed. Imported veterinary devices must be labeled purchase animals from licensed dealers.
“for veterinary use only” and radiation‐emitting devices • Set regulations on animal environmental conditions
are verified and registered according to the radiologic for housing in and transportation to research and
health regulations. teaching facilities.