Page 15 - E-MODUL FUNGSI KOMPOSISI DAN FUNGSI INVERS
P. 15
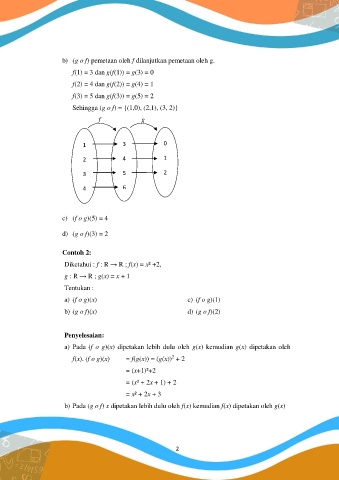
b) (g o f) pemetaan oleh f dilanjutkan pemetaan oleh g.
f(1) = 3 dan g(f(1)) = g(3) = 0
f(2) = 4 dan g(f(2)) = g(4) = 1
f(3) = 5 dan g(f(3)) = g(5) = 2
Sehingga (g o f) = {(1,0), (2,1), (3, 2)}
f g
1 3 0
2 4 1
3 5 2
4 6
c) (f o g)(5) = 4
d) (g o f)(3) = 2
Contoh 2:
Diketahui : f : R → R ; f(x) = x² +2,
g : R → R ; g(x) = x + 1
Tentukan :
a) (f o g)(x) c) (f o g)(1)
b) (g o f)(x) d) (g o f)(2)
Penyelesaian:
a) Pada (f o g)(x) dipetakan lebih dulu oleh g(x) kemudian g(x) dipetakan oleh
2
f(x). (f o g)(x) = f(g(x)) = (g(x)) + 2
= (x+1)²+2
= (x² + 2x + 1) + 2
= x² + 2x + 3
b) Pada (g o f) x dipetakan lebih dulu oleh f(x) kemudian f(x) dipetakan oleh g(x)
2