Page 212 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 212
Causes Consequences
More agricultural
More agricultural production Habitat alteration
production
Decline in Loss of biodiversity
death rates and ecosystem
New services
technologies More resource
extraction,
Better medical care manufacturing, Global climate
and consumption change
Better sanitation
Human population
growth More fossil
fuel use
More waste and
pollution
Historic need for Birth rates
farm labor
remain high Economic loss
Denser populations
Restrictions on Health impacts
women’s rights
Social disruption
Prohibitions on War, conflict,
birth control refugees
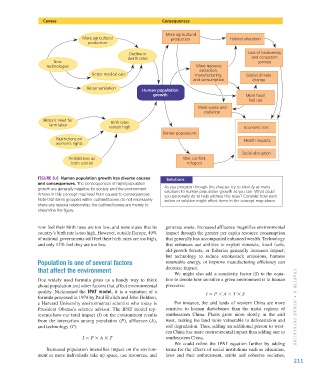
Figure 8.6 Human population growth has diverse causes Solutions
and consequences. The consequences of rapid population
growth are generally negative for society and the environment. As you progress through this chapter, try to identify as many
Arrows in this concept map lead from causes to consequences. solutions to human population growth as you can. What could
you personally do to help address this issue? Consider how each
Note that items grouped within outlined boxes do not necessarily action or solution might affect items in the concept map above.
share any special relationship; the outlined boxes are merely to
streamline the figure.
now feel their birth rates are too low, and none states that its generate waste. Increased affluence magnifies environmental
country’s birth rate is too high. However, outside Europe, 49% impact through the greater per capita resource consumption
of national governments still feel their birth rates are too high, that generally has accompanied enhanced wealth. Technology
and only 12% feel they are too low. that enhances our abilities to exploit minerals, fossil fuels,
old-growth forests, or fisheries generally increases impact,
but technology to reduce smokestack emissions, harness
Population is one of several factors renewable energy, or improve manufacturing efficiency can
that affect the environment decrease impact.
We might also add a sensitivity factor (S) to the equa-
One widely used formula gives us a handy way to think tion to denote how sensitive a given environment is to human
about population and other factors that affect environmental pressures:
quality. Nicknamed the iPAT model, it is a variation of a I 5 P 3 A 3 T 3 S
formula proposed in 1974 by Paul Ehrlich and John Holdren,
a Harvard University environmental scientist who today is For instance, the arid lands of western China are more
President Obama’s science advisor. The IPAT model rep- sensitive to human disturbance than the moist regions of CHAPTER 8 • Hum A n Po P ul AT i on
resents how our total impact (I) on the environment results southeastern China. Plants grow more slowly in the arid
from the interaction among population (P), affluence (A), west, making the land more vulnerable to deforestation and
and technology (T): soil degradation. Thus, adding an additional person to west-
ern China has more environmental impact than adding one to
I 5 P 3 A 3 T southeastern China.
We could refine the IPAT equation further by adding
Increased population intensifies impact on the environ- terms for the effects of social institutions such as education,
ment as more individuals take up space, use resources, and laws and their enforcement, stable and cohesive societies,
211
M08_WITH7428_05_SE_C08.indd 211 12/12/14 2:58 PM