Page 216 - Environment: The Science Behind the Stories
P. 216
Persons/km 2
0 25–249
1–4 250–999
5–24 1000+
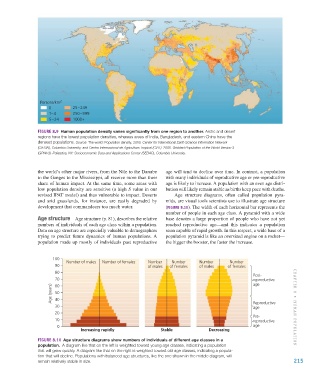
Figure 8.9 Human population density varies significantly from one region to another. Arctic and desert
regions have the lowest population densities, whereas areas of India, Bangladesh, and eastern China have the
densest populations. Source: The world: Population density, 2000. Center for International Earth Science Information Network
(CIESIN), Columbia University; and Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT). 2005. Gridded Population of the World Version 3
(GPWv3). Palisades, NY: Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC), Columbia University.
the world’s other major rivers, from the Nile to the Danube age will tend to decline over time. In contrast, a population
to the Ganges to the Mississippi, all receive more than their with many individuals of reproductive age or pre-reproductive
share of human impact. At the same time, some areas with age is likely to increase. A population with an even age distri-
low population density are sensitive (a high S value in our bution will likely remain stable as births keep pace with deaths.
revised IPAT model) and thus vulnerable to impact. Deserts Age structure diagrams, often called population pyra-
and arid grasslands, for instance, are easily degraded by mids, are visual tools scientists use to illustrate age structure
development that commandeers too much water. (Figure 8.10). The width of each horizontal bar represents the
number of people in each age class. A pyramid with a wide
Age structure Age structure (p. 81), describes the relative base denotes a large proportion of people who have not yet
numbers of individuals of each age class within a population. reached reproductive age—and this indicates a population
Data on age structure are especially valuable to demographers soon capable of rapid growth. In this respect, a wide base of a
trying to predict future dynamics of human populations. A population pyramid is like an oversized engine on a rocket—
population made up mostly of individuals past reproductive the bigger the booster, the faster the increase.
100
Number of males Number of females Number Number Number Number
90 of males of females of males of females
80
Post-
70 reproductive
age
60
Age (years) 50
40
30 Reproductive CHAPTER 8 • Hum A n Po P ul AT i on
age
20
Pre-
10 reproductive
0 age
Increasing rapidly Stable Decreasing
Figure 8.10 Age structure diagrams show numbers of individuals of different age classes in a
population. A diagram like that on the left is weighted toward young age classes, indicating a population
that will grow quickly. A diagram like that on the right is weighted toward old age classes, indicating a popula-
tion that will decline. Populations with balanced age structures, like the one shown in the middle diagram, will
remain relatively stable in size. 215
M08_WITH7428_05_SE_C08.indd 215 12/12/14 2:58 PM