Page 681 - Basic Electrical Engineering
P. 681
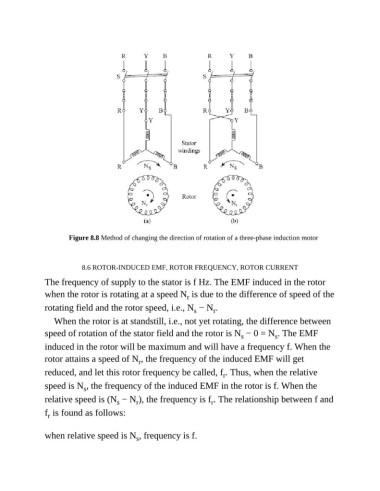
Figure 8.8 Method of changing the direction of rotation of a three-phase induction motor
8.6 ROTOR-INDUCED EMF, ROTOR FREQUENCY, ROTOR CURRENT
The frequency of supply to the stator is f Hz. The EMF induced in the rotor
when the rotor is rotating at a speed N is due to the difference of speed of the
r
rotating field and the rotor speed, i.e., N − N .
r
s
When the rotor is at standstill, i.e., not yet rotating, the difference between
speed of rotation of the stator field and the rotor is N − 0 = N . The EMF
s
s
induced in the rotor will be maximum and will have a frequency f. When the
rotor attains a speed of N , the frequency of the induced EMF will get
r
reduced, and let this rotor frequency be called, f . Thus, when the relative
r
speed is N , the frequency of the induced EMF in the rotor is f. When the
s
relative speed is (N − N ), the frequency is f . The relationship between f and
r
r
s
f is found as follows:
r
when relative speed is N , frequency is f.
s