Page 252 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 252
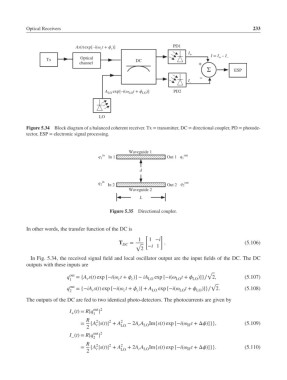
Optical Receivers 233
As(t)exp[–i(ω c t + ϕ )] PD1
c
I + I = I – I
Tx Optical DC + –
channel +
Σ ESP
–
I –
A LO exp[–i(ω t + ϕ )] PD2
LO
LO
LO
Figure 5.34 Block diagram of a balanced coherent receiver. Tx = transmitter, DC = directional coupler, PD = photode-
tector, ESP = electronic signal processing.
Waveguide 1
q 1 in In 1 Out 1 q 1 out
d
q 2 in In 2 Out 2 q 2 out
Waveguide 2
L
Figure 5.35 Directional coupler.
In other words, the transfer function of the DC is
[ ]
1 1 −i
T . (5.106)
DC = √ −i 1
2
In Fig. 5.34, the received signal field and local oscillator output are the input fields of the DC. The DC
outputs with these inputs are
√
q out ={A s(t) exp [−i( t + )] − iA exp [−i( t + )]}∕ 2, (5.107)
1 r c c LO LO LO
√
q out ={−iA s(t) exp [−i( t + )] + A exp [−i( t + )]}∕ 2. (5.108)
2 r c c LO LO LO
The outputs of the DC are fed to two identical photo-detectors. The photocurrents are given by
out 2
I (t)= R|q |
+ 1
R 2 2 2
= {A |s(t)| + A − 2A A Im{s(t) exp [−i( t +Δ)]}}, (5.109)
IF
r
r LO
2 LO
out 2
−
I (t)= R|q |
2
R 2 2 2
= {A |s(t)| + A + 2A A Im{s(t) exp [−i( t +Δ)]}}. (5.110)
r
r LO
IF
2 LO