Page 455 - Fiber Optic Communications Fund
P. 455
436 Fiber Optic Communications
( )
T
2
P(t)= P peak sech . (10.120)
T 0
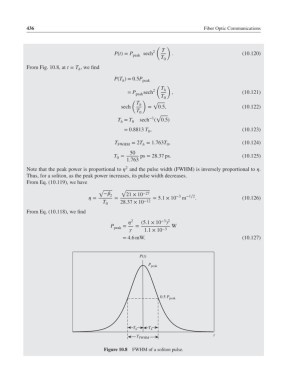
From Fig. 10.8, at t = T , we find
h
P(T )= 0.5P
h peak
( )
T h
2
= P peak sech , (10.121)
T 0
( )
T h √
sech = 0.5, (10.122)
T 0
√
−1
T = T 0 sech ( 0.5)
h
= 0.8813 T , (10.123)
0
T = 2T = 1.763T , (10.124)
FWHM h 0
50
T = ps = 28.37 ps. (10.125)
0
1.763
2
Note that the peak power is proportional to and the pulse width (FWHM) is inversely proportional to .
Thus, for a soliton, as the peak power increases, its pulse width decreases.
From Eq. (10.119), we have
√ √
− 2 21 × 10 −27
= = = 5.1 × 10 −3 m −1∕2 . (10.126)
T 28.37 × 10 −12
0
From Eq. (10.118), we find
−3 2
2 (5.1 × 10 )
P peak = = W
1.1 × 10 −3
= 4.6 mW. (10.127)
P(t)
P peak
0.5 P peak
T h T h
t
T FWHM
Figure 10.8 FWHM of a soliton pulse.