Page 32 - CCFA Journal - Ninth Issue
P. 32
风险管理 Risk Management 加中金融
Stress Testing and Credit Provisioning for Canadian Banks
加拿大银行的压力测试和信贷拨备
【作者及翻译】Jeff Huang, Scotia Bank; Xin Liang, Equitable Bank
Credit risk management in the banking book 银行账簿的信用风险管理
In Canada (and most of other countries), the largest risk exposure banks are subject to is credit risk, roughly accounting for 80% of
total quantifiable risks as evidenced by banks’ capital disclosure (Table 1). The major contribution of credit risk is from the banking
book, which are assets on the balance sheet that are expected to be held to maturity. In the banking book the wholesale portfolio
is usually comprised of businesses, sovereigns, public sector entities, banks and other financial institutions, as well as certain high
net value individuals. The retail portfolio is comprised of residential mortgages, personal loans, credit cards, and small business
loans.
Credit risk is quantified at both the individual obligor and portfolio levels to manage expected credit losses and minimize unexpected
losses to limit earning volatility and ensure that the bank is adequately capitalized. Unexpected loss for at pre-determined
confidence interval is used to measure capital requirement. Expected loss for credit products are often referred to as allowance for
credit loss (AOL) in accounting.
At the bank level, there are three critical processes in credit risk management, which are economic and regulatory capital, stress
testing, and credit provisioning. In this paper, we will focus on the latter two, which have been playing a central role in managing
the credit risk during the pandemic. Capital reflects a long term, through the cycle view, and therefore, does not change materially
due to specific economic events.
在加拿大等多数国家,银行最大的风险敞口是信用风险,从银行的资本披露可以看出,约 90%可量化的风险为信用风险,
详见表 1。信用风险主要源自银行账户,即资产负债表上预计持有至到期的资产。在银行账户内,机构业务资产池通常包
括企业、银行账簿主权国家、公共部门实体、银行和其他金融机构,以及特定高净值个人客户。零售业务资产池包括住宅
抵押贷款、个人贷款、信用卡和小企业贷款。
预期损失通常指会计上的信用风险损失准备金。为管理预期信用损失,银行从单个债务人和投资组合两个层面量化信用风
险。
非预期损失指银行在特定置信区间下所需的资本水平。银行通过限制收益波动最小化非预期损失,以确保银行资本水平充
足。
在银行层面,管理信贷风险有三大支柱,即经济和监管资本、压力测试和风险拨备。在本文中,我们将重点讨论后两者,
它们在疫情期间在管理信贷风险方面发挥了核心作用。资本反映了一个长期的周期观点,因此不会因特定的经济事件而发
生重大变化。
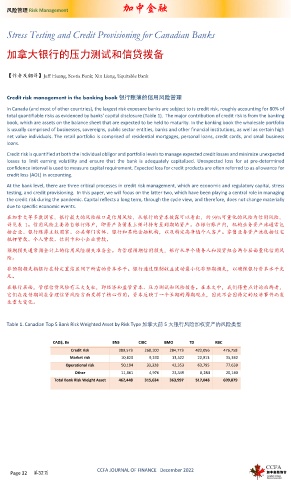
Table 1. Canadian Top 5 Bank Risk Weighted Asset by Risk Type 加拿大前 5 大银行风险加权资产的风险类型
CAD$, Bn BNS CIBC BMO TD RBC
Credit risk 389,573 268,100 284,773 422,056 476,758
Market risk 10,820 9,230 13,522 22,913 35,342
Operational risk 50,194 33,328 42,353 63,795 77,639
Other 11,861 4,976 23,349 8,284 20,140
Total Bank Risk Weight Asset 462,448 315,634 363,997 517,048 609,879
CCFA JOURNAL OF FINANCE December 2022
Page 32 第32页