Page 61 - FINAL CFA SLIDES JUNE 2019 DAY 2
P. 61
LOS 8.k: Describe the relative locations Session Unit 2:
of the mean, median, and mode for a 8. Statistical Concepts and Market Returns (B)
unimodal, non-symmetrical distribution.
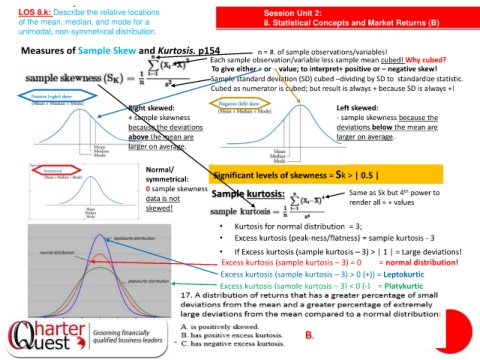
Measures of Sample Skew and Kurtosis. p154 n = #. of sample observations/variables!
Each sample observation/variable less sample mean cubed! Why cubed?
To give either + or – value; to interpret+ positive or – negative skew!
Sample standard deviation (SD) cubed –dividing by SD to standardize statistic.
Cubed as numerator is cubed; but result is always + because SD is always +!
Right skewed: Left skewed:
+ sample skewness - sample skewness because the
because the deviations deviations below the mean are
above the mean are larger on average.
larger on average.
Normal/
symmetrical: Significant levels of skewness = Sk > | 0.5 |
0 sample skewness Sample kurtosis: Same as Sk but 4 power to
th
data is not
render all = + values
skewed!
• Kurtosis for normal distribution = 3;
• Excess kurtosis (peak-ness/flatness) = sample kurtosis - 3
• If Excess kurtosis (sample kurtosis – 3) > | 1 | = Large deviations!
Excess kurtosis (sample kurtosis – 3) = 0 = normal distribution!
Excess kurtosis (sample kurtosis – 3) > 0 (+)) = Leptokurtic
Excess kurtosis (sample kurtosis – 3) < 0 (-) = Platykurtic
B.