Page 134 - phytochemistry I - PharmD Clinical
P. 134
Dicoumarols are dimers of 4-hydroxycoumarins. They are powerful oral
anticoagulants such as: acenocoumarol, phenprocoumon, warfarin.
Mechanism of anticoagulant activity:
Dicoumarols arecompetitive inhibitor of vitamin K epoxide reductase, an
enzyme that recycles vitamin K, thus causing depletion of active vitamin
K in blood. This prevents the formation of the active form of prothrombin
and several other coagulant enzymes.
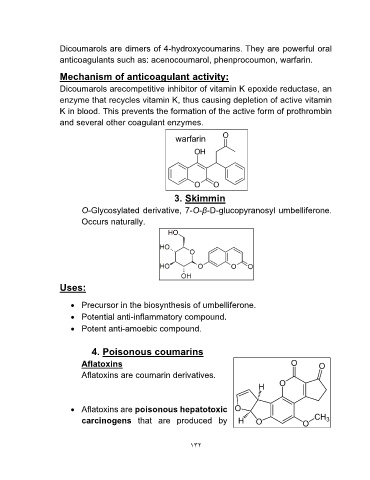
warfarin
3. Skimmin
O-Glycosylated derivative, 7-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl umbelliferone.
Occurs naturally.
Uses:
• Precursor in the biosynthesis of umbelliferone.
• Potential anti-inflammatory compound.
• Potent anti-amoebic compound.
4. Poisonous coumarins
Aflatoxins
Aflatoxins are coumarin derivatives.
• Aflatoxins are poisonous hepatotoxic
carcinogens that are produced by
۱۳۲