Page 136 - phytochemistry I - PharmD Clinical
P. 136
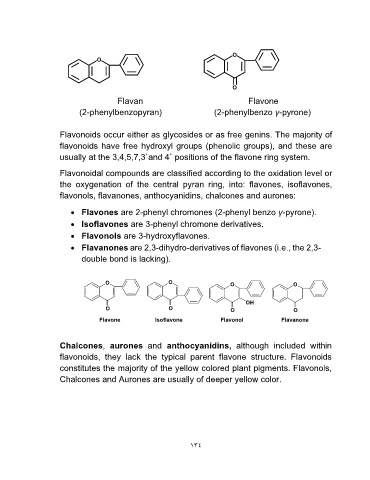
O
O
Flavan O
(2-phenylbenzopyran)
Flavone
(2-phenylbenzo γ-pyrone)
Flavonoids occur either as glycosides or as free genins. The majority of
flavonoids have free hydroxyl groups (phenolic groups), and these are
usually at the 3,4,5,7,3`and 4` positions of the flavone ring system.
Flavonoidal compounds are classified according to the oxidation level or
the oxygenation of the central pyran ring, into: flavones, isoflavones,
flavonols, flavanones, anthocyanidins, chalcones and aurones:
• Flavones are 2-phenyl chromones (2-phenyl benzo γ-pyrone).
• Isoflavones are 3-phenyl chromone derivatives.
• Flavonols are 3-hydroxyflavones.
• Flavanones are 2,3-dihydro-derivatives of flavones (i.e., the 2,3-
double bond is lacking).
O O O O
O O OH O
Flavone Isoflavone O Flavanone
Flavonol
Chalcones, aurones and anthocyanidins, although included within
flavonoids, they lack the typical parent flavone structure. Flavonoids
constitutes the majority of the yellow colored plant pigments. Flavonols,
Chalcones and Aurones are usually of deeper yellow color.
۱۳٤