Page 137 - phytochemistry I - PharmD Clinical
P. 137
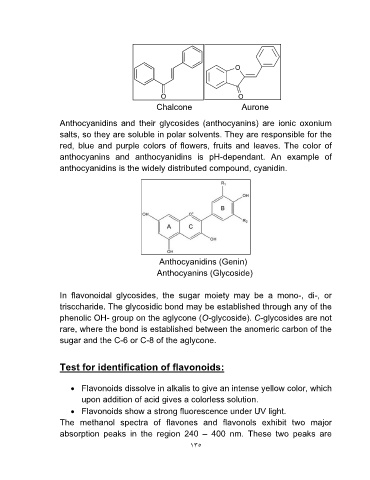
Chalcone Aurone
Anthocyanidins and their glycosides (anthocyanins) are ionic oxonium
salts, so they are soluble in polar solvents. They are responsible for the
red, blue and purple colors of flowers, fruits and leaves. The color of
anthocyanins and anthocyanidins is pH-dependant. An example of
anthocyanidins is the widely distributed compound, cyanidin.
Anthocyanidins (Genin)
Anthocyanins (Glycoside)
In flavonoidal glycosides, the sugar moiety may be a mono-, di-, or
trisccharide. The glycosidic bond may be established through any of the
phenolic OH- group on the aglycone (O-glycoside). C-glycosides are not
rare, where the bond is established between the anomeric carbon of the
sugar and the C-6 or C-8 of the aglycone.
Test for identification of flavonoids:
• Flavonoids dissolve in alkalis to give an intense yellow color, which
upon addition of acid gives a colorless solution.
• Flavonoids show a strong fluorescence under UV light.
The methanol spectra of flavones and flavonols exhibit two major
absorption peaks in the region 240 – 400 nm. These two peaks are
۱۳٥