Page 143 - phytochemistry I - PharmD Clinical
P. 143
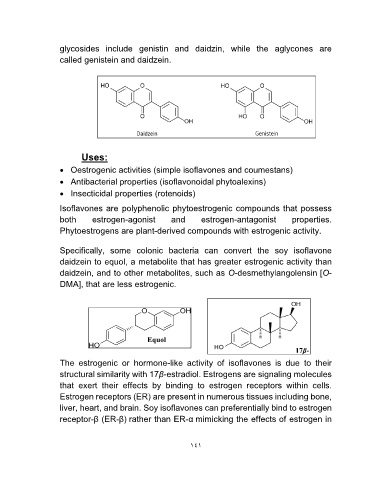
glycosides include genistin and daidzin, while the aglycones are
called genistein and daidzein.
Uses:
• Oestrogenic activities (simple isoflavones and coumestans)
• Antibacterial properties (isoflavonoidal phytoalexins)
• Insecticidal properties (rotenoids)
Isoflavones are polyphenolic phytoestrogenic compounds that possess
both estrogen-agonist and estrogen-antagonist properties.
Phytoestrogens are plant-derived compounds with estrogenic activity.
Specifically, some colonic bacteria can convert the soy isoflavone
daidzein to equol, a metabolite that has greater estrogenic activity than
daidzein, and to other metabolites, such as O-desmethylangolensin [O-
DMA], that are less estrogenic.
Equol
17β-
The estrogenic or hormone-like activity of isoflavones is due to their
structural similarity with 17β-estradiol. Estrogens are signaling molecules
that exert their effects by binding to estrogen receptors within cells.
Estrogen receptors (ER) are present in numerous tissues including bone,
liver, heart, and brain. Soy isoflavones can preferentially bind to estrogen
receptor-β (ER-β) rather than ER-α mimicking the effects of estrogen in
۱٤۱