Page 201 - 00. Complete Version - Progress Report IPEN 2014-2016
P. 201
Nuclear Science and Technology | Progress Report 201
tracers of marine processes, as ground water increase of water column depth and ranged
discharge. The activity concentrations of Ra, from 0.049 cm·y1 to 0.40 cm·y1.
226
228 Ra and Pb in four short marine cores, col-
210
lected from the continental platform to up- Radon as an indicator of environmental
per slope of Southwest Atlantic Ocean, were contamination by hydrocarbons in free-phase
determined. Taking into account the results
obtained, sedimentation rates and the ages
of each sediment layer were determined us-
ing the geochronological dating method with
210 Pb. All sediment samples were totally ac-
id-digested in microwave. The sequential ra-
diochemical separation of 226 Ra, 228 Ra, 210 Pb
were performed, obtaining in the end the pre-
cipitation of Ba(Ra)SO4 and PbCrO4. The gross
δ measurements of 226 Ra and gross δ mea-
210
surements of Ra and Pb from the precipi-
228
tates were carried out in a gas-flow low back-
ground proportional counter. Concerning all
cores analyzed, the activities concentrations of
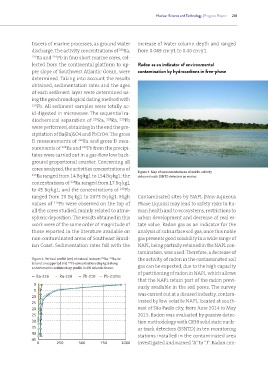
Figure 3. Map of isoconcentrations of 222Rn activity
226 Ra ranged from 14 Bq·kg1 to 154 Bq·kg1; the obtained with SSNTD detectors in winter.
228
concentrations of Ra ranged from 17 Bq·kg1
to 45 Bq·kg1; and the concentrations of 210 Pb
ranged from 20 Bq·kg1 to 2073 Bq·kg1. High Contaminated sites by NAPL (Non-Aqueous
values of 210 Pb were observed on the top of Phase Liquids) may lead to safety risks to hu-
all the cores studied, mainly related to atmo- man health and to ecosystems, restrictions to
spheric deposition. The results obtained in this urban development and decrease of real es-
work were of the same order of magnitude of tate value. Radon gas as an indicator for the
those reported in the literature available on analysis of subsurface soil gas, once this noble
non-contaminated areas of Southeast Brazil- gas presents good solubility in a wide range of
ian Coast. Sedimentation rates fall with the NAPL, being partially retained in the NAPL con-
tamination, was used. Therefore, a decrease of
Figure 2. Vertical profile (cm) of natural isotopes Ra, Ra, to- the activity of radon in the contaminated soil
228
226
tal and unsupported (ns) Pb concentrations (Bq·kg1) along gas can be expected, due to the high capacity
210
a short marine sedimentary profile in SW Atlantic Ocean.
of partitioning of radon in NAPL, which allows
Ra-226 Ra-228 Pb-210 Pb-210ns
that the NAPL retain part of the radon previ-
0 ously available in the soil pores. The survey
5
20 was carried out at a disused industry, contam-
25 inated by low volatile NAPL, located at south-
20 east of São Paulo city, from June 2014 to May
25 2015. Radon was evaluated by passive detec-
30 tion methodology with CR39 solid state nucle-
35 ar track detectors (SSNTD) in ten monitoring
40
stations installed in the contaminated area
45
0 250 500 750 1000 investigated and named “A” to “J”. Radon con-