Page 39 - The World About Us
P. 39
Empire in pink
2.1.2
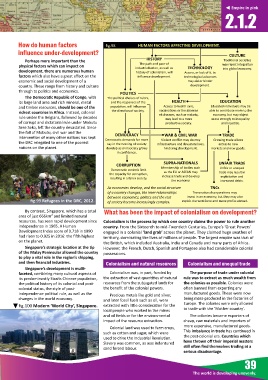
How do human factors fig.98 HUMAN FACTORS AFFECTING DEVELOPMENT.
influence under-development?
CULTURE
HISTORY
Perhaps more important than the Tradi onal socie es
The path and pace of
physical factors which can impact on industrialisa on, as well as TECHNOLOGY may reject integra on
into global economy.
development, there are numerous human history of colonialism, will Access, or lack of it, to
factors which also have a great effect on the influence development. technological advances
economic and social development of a may aid or hinder
country. These range from history and culture development.
through to poli cs and economics.
POLITICS
The Democra c Republic of Congo, with The poli cal choices of rulers,
its large land area and rich mineral, metal and the responses of the HEALTH EDUCATION
and mber resources, should be one of the popula on, will influence Access to health care, Educated individuals may be
richest countries in Africa. Instead, colonial the direc on of society. vaccina ons or the absence able to contribute more to the
of diseases, such as malaria, economy, but may object
rule under the Belgians, followed by decades may lead to a more more strongly to inequality
of corrupt and dictatorial rule under Mobutu produc ve society. and injus ce.
Sese Seko, le the country devastated. Since
the fall of Mobutu, civil war and the
DEMOCRACY
TRADE
WAR & CIVIL WAR
interven on of many other na ons has kept Democra c demands for more Violent conflict may destroy Growing trade allows
the DRC relegated to one of the poorest say in the running of society infrastructure and devastate lives, access to new
na ons on the planet. develop as civil society grows hindering development. markets and new goods.
in confidence.
SUPRA-NATIONALS UNFAIR TRADE
CORRUPTION
Democra c controls limit Membership of bodies such Unfair or unequal
the capacity for corrup on, as the EU or ASEAN may trade may result in
resul ng in a fairer society. increase trade and develop exploita on and
the economy. increased debts.
fig.95 As economies develop, and the social structure TNCs
of a country changes, the inter-rela onships Transna onal corpora ons may
between economics, poli cs and the rest invest in an economy, but they may also
fig.99 Refugees in the DRC, 2012. of society become increasingly complex. exploit the workforce and move profits abroad.
By contrast, Singapore, which has a total What has been the impact of colonialism on development?
area of just 666km² and limited natural
resources, has seen rapid development since Colonialism is the process by which one country claims the power to rule another
independence in 1965. A Human country. From the Sixteenth to mid-Twen eth Centuries, Europe’s ‘Great Powers’
Development Index score of 0.718 in 1990 engaged in a colonial ‘land grab’ across the planet. They claimed huge swathes of
had risen to 0.925 in 2016: the fi h highest territory, domina ng the lives of millions of people. The largest empire was that of
on the planet.
the Bri sh, which included Australia, India and Canada and many parts of Africa.
Singapore’s strategic loca on at the p However, the French, Dutch, Spanish and Portugese also had considerable colonial
of the Malay Peninsular allowed the country possessions.
to play a vital role in the region’s shipping,
and then financial industries. Colonialism and natural resources Colonialism and unequal trade
Singapore’s development is mul -
faceted, combining many cultural aspects of Colonialism was, in part, funded by The purpose of trade under colonial
its predominantly Straits Chinese popula on, the extrac on of vast quan es of natural rule was to extract as much wealth from
the poli cal history of its colonial and post- resources from the subjugated lands for the colonies as possible. Colonies were
colonial status, the style of post- the benefit of the colonial powers. o en banned from expor ng any
independence poli cal rule, as well as the Precious metals like gold and silver, manufactured goods. These were now
changes in the world economy. and later fossil fuels such as oil, were being mass-produced in the factories of
fig.100 Modern ‘World City’, Singapore. extracted with li le considera on for the Europe. The colonies were only allowed
local people who worked in the mines to trade with the ‘Mother country’.
and oil fields or for the environmental The colonies became exporters of
impact of the resource extrac on. cheap, raw materials and importers of
more expensive, manufactured goods.
Colonial land was used to farm crops,
such as co on and sugar, which were This imbalance in trade has con nued in
used to drive the Industrial Revolu on. the post-colonial era. Countries which
Slavery was common, as was indentured have thrown off their imperial masters
sand forced labour. s ll o en find themselves trading at a
serious disadvantage.
39
The world is developing unevenly.