Page 427 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 427
P1: FAW
BLUK007-11 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:5 Char Count= 0
Chapter 11: Dopamine and prolactin axis 423
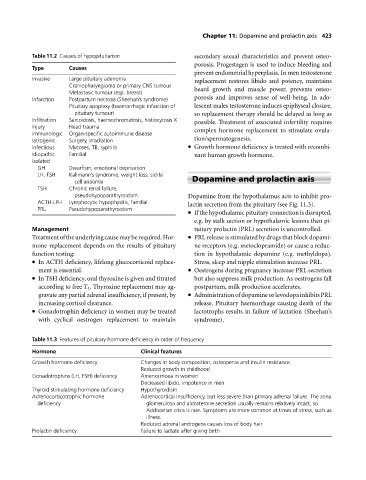
Table 11.2 Causes of hypopituitarism secondary sexual characteristics and prevent osteo-
porosis. Progestagen is used to induce bleeding and
Type Causes
prevent endometrial hyperplasia. In men testosterone
Invasive Large pituitary adenoma replacement restores libido and potency, maintains
Craniopharyngioma or primary CNS tumour beard growth and muscle power, prevents osteo-
Metastasic tumour (esp. breast)
Infarction Postpartum necrosis (Sheehan’s syndrome) porosis and improves sense of well-being. In ado-
Pituitary apoplexy (haemorrhagic infarction of lescent males testosterone induces epiphyseal closure,
pituitary tumour) so replacement therapy should be delayed as long as
Infiltration Sarcoidosis, haemochromatosis, histiocytosis X possible. Treatment of associated infertility requires
Injury Head trauma complex hormone replacement to stimulate ovula-
Immunologic Organ-specific autoimmune disease
Iatrogenic Surgery, irradiation tion/spermatogenesis.
Infectious Mycoses, TB, syphilis Growth hormone deficiency is treated with recombi-
Idiopathic Familial nant human growth hormone.
Isolated
GH Dwarfism, emotional deprivation
LH, FSH Kallmann’s syndrome, weight loss, sickle
cell anaemia Dopamine and prolactin axis
TSH Chronic renal failure,
pseudohypoparathyroidism Dopamine from the hypothalamus acts to inhibit pro-
ACTH-LPH Lymphocytic hypophysitis, familial lactin secretion from the pituitary (see Fig. 11.3).
PRL Pseudohypoparathyroidism
If the hypothalamic pituitary connection is disrupted,
e.g. by stalk section or hypothalamic lesions then pi-
Management tuitary prolactin (PRL) secretion is uncontrolled.
Treatmentoftheunderlyingcausemayberequired.Hor- PRL release is stimulated by drugs that block dopami-
mone replacement depends on the results of pituitary ne receptors (e.g. metoclopramide) or cause a reduc-
function testing: tion in hypothalamic dopamine (e.g. methyldopa).
In ACTH deficiency, lifelong glucocorticoid replace- Stress, sleep and nipple stimulation increase PRL.
ment is essential. Oestrogens during pregnancy increase PRL secretion
In TSHdeficiency, oral thyroxine is given and titrated but also suppress milk production. As oestrogens fall
according to free T 4 .Thyroxine replacement may ag- postpartum, milk production accelerates.
gravate any partial adrenal insufficiency, if present, by AdministrationofdopamineorlevodopainhibitsPRL
increasing cortisol clearance. release. Pituitary haemorrhage causing death of the
Gonadotrophin deficiency in women may be treated lactotrophs results in failure of lactation (Sheehan’s
with cyclical oestrogen replacement to maintain syndrome).
Table 11.3 Features of pituitary hormone deficiency in order of frequency
Hormone Clinical features
Growth hormone deficiency Changes in body composition, osteopenia and insulin resistance
Reduced growth in childhood
Gonadotrophins (LH, FSH) deficiency Amenorrhoea in women
Decreased libido, impotence in men
Thyroid stimulating hormone deficiency Hypothyroidism
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone Adrenocortical insufficiency, but less severe than primary adrenal failure. The zona
deficiency glomerulosa and aldosterone secretion usually remains relatively intact, so
Addisonian crisis is rare. Symptoms are more common at times of stress, such as
illness.
Reduced adrenal androgens causes loss of body hair
Prolactin deficiency Failure to lactate after giving birth