Page 429 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 429
P1: FAW
BLUK007-11 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:5 Char Count= 0
Chapter 11: Growth axis 425
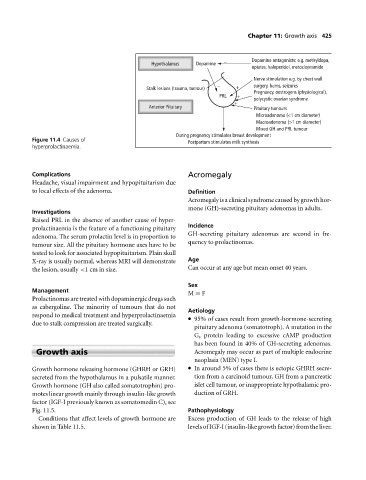
− Dopamine antagonists: e.g. methyldopa,
Hypothalamus Dopamine
opiates, haloperidol, metoclopramide
Nerve stimulation e.g. by chest wall
− surgery, burns, seizures
Stalk lesions (trauma, tumour) + Pregnancy, oestrogens (physiological),
PRL + polycystic ovarian syndrome
+
Anterior Pituitary Pituitary tumours
Microadenoma (<1 cm diameter)
Macroadenoma (>1 cm diameter)
Mixed GH and PRL tumour
During pregnancy stimulates breast development
Figure 11.4 Causes of Postpartum stimulates milk synthesis
hyperprolactinaemia.
Complications Acromegaly
Headache, visual impairment and hypopituitarism due
to local effects of the adenoma. Definition
Acromegaly is a clinical syndrome caused by growth hor-
mone (GH)-secreting pituitary adenomas in adults.
Investigations
Raised PRL in the absence of another cause of hyper-
Incidence
prolactinaemia is the feature of a functioning pituitary
GH-secreting pituitary adenomas are second in fre-
adenoma. The serum prolactin level is in proportion to
quency to prolactinomas.
tumour size. All the pituitary hormone axes have to be
tested to look for associated hypopituitarism. Plain skull
X-ray is usually normal, whereas MRI will demonstrate Age
the lesion, usually <1cmin size. Can occur at any age but mean onset 40 years.
Sex
Management
M = F
Prolactinomasaretreatedwithdopaminergicdrugssuch
as cabergoline. The minority of tumours that do not
Aetiology
respond to medical treatment and hyperprolactinaemia
95% of cases result from growth-hormone-secreting
due to stalk compression are treated surgically.
pituitary adenoma (somatotroph). A mutation in the
G s protein leading to excessive cAMP production
has been found in 40% of GH-secreting adenomas.
Growth axis Acromegaly may occur as part of multiple endocrine
neoplasia (MEN) type I.
Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH or GRH) In around 5% of cases there is ectopic GHRH secre-
secreted from the hypothalamus in a pulsatile manner. tion from a carcinoid tumour, GH from a pancreatic
Growth hormone (GH also called somatotrophin) pro- islet cell tumour, or inappropriate hypothalamic pro-
motes linear growth mainly through insulin-like growth duction of GRH.
factor (IGF-I previously known as somatomedin C), see
Fig. 11.5. Pathophysiology
Conditions that affect levels of growth hormone are Excess production of GH leads to the release of high
shown in Table 11.5. levels of IGF-I (insulin-like growth factor) from the liver.