Page 432 - Medicine and Surgery
P. 432
P1: FAW
BLUK007-11 BLUK007-Kendall May 25, 2005 8:5 Char Count= 0
428 Chapter 11: Endocrine system
Table 11.6 Disorders of thyroid axis
Increased hormone Decreased hormone
TSH Hypothyroidism (thyroid failure and lack of Primary thyrotoxicosis, e.g. Graves’ disease, toxic
feedback) multinodular goitre (due to increased thyroid
TSH secreting pituitary adenoma (rare) hormone negative feedback)
Thyroid hormone resistance
T 3 and T 4 Graves’ disease Hashimoto’s disease
Toxic multinodular goitre Iatrogenic: following thyroidectomy or radioiodine treatment
Early Hashimoto’s disease Iodine deficiency
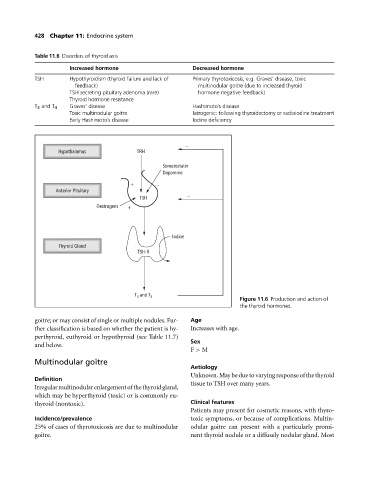
−
Hypothalamus TRH
Somatostatin
Dopamine
+ −
Anterior Pituitary
TSH −
Oestrogens +
Iodine
Thyroid Gland
TSH-R
T 4 and T 3
Figure 11.6 Production and action of
the thyroid hormones.
goitre; or may consist of single or multiple nodules. Fur- Age
ther classification is based on whether the patient is hy- Increases with age.
perthyroid, euthyroid or hypothyroid (see Table 11.7)
Sex
and below.
F > M
Multinodular goitre
Aetiology
Unknown.Maybeduetovaryingresponseofthethyroid
Definition
tissue to TSH over many years.
Irregularmultinodularenlargementofthethyroidgland,
which may be hyperthyroid (toxic) or is commonly eu-
thyroid (nontoxic). Clinical features
Patients may present for cosmetic reasons, with thyro-
Incidence/prevalence toxic symptoms, or because of complications. Multin-
25% of cases of thyrotoxicosis are due to multinodular odular goitre can present with a particularly promi-
goitre. nent thyroid nodule or a diffusely nodular gland. Most